Luna User Manual
A full guide to all User functions of the Luna OS6 system
Terminology and Acronyms
This document will refer to words and acronyms. The lists below give a brief explanation of each.
Acronyms
| Acronym | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CU | Control Unit |
| PU | Processing Unit |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| OPS | Optical Processing System |
| IU | Interrogator Unit |
| DAS | Distributed Acoustic Sensing |
| KP / MP | Kilometre / Mile Point |
| OS | Operating System |
| TOTP | Time-based One-Time Password |
Terminology
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Control Unit | A Windows-based PC built specifically to run the OS6 software and monitor an asset. |
| Processing Unit | A server specifically to process/store the data from the Interrogator Unit |
| Interrogator Unit | An Luna proprietary product that connects to the fibre and performs Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) measurements |
| Cursor | The position indicator on the computer screen that is moved by use of the mouse |
| Desktop | This is the large display area that appears when the CU is activated. On it there are different icons that provide to access different functions |
| Graphical User Interface | The Luna software presented to the user on the CU |
| Icon | This is a picture that represents a function that can be carried out on the computer. Click on an icon to activate its function |
| Layer | Layers are used in the map window to show and hide different types of visual information |
| Optical Processing System | A multi-component system comprising an Interrogator Unit and Processing Unit. |
| Tab | This is an access link to different pages within a window covering different areas of interest as represented by the tab heading |
| Toolbar | This is a menu bar where the menu items are presented as icons |
| Task Bar | This is the bar that runs along the base of the window which shows which applications are running |
| Status Bar | This is a bar at the bottom of a Window that displays status information to the user. It often pertains to the mouse position |
| Pane | This is a region of a window defined by a border, used to display data |
| Window | An area on the screen that displays information for a specific program. A typical window includes a title bar along the top that describes the contents of the window, followed by a menu bar and toolbar. Most of the window's remaining area is a pane(s) used to display the content. |
| Histogram | A chart displayed in real time on the Surveillance Waterfall Window. It represents the amplitude of the sound observed by each channel. |
| Waterfall | A dynamic chart that represents live & historical data from the histogram. Location is represented along the x-axis; time is shown on the y-axis and amplitude of the signal is represented by varying colours. |
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide a user the information required to monitor an asset using Luna OS6 software. It provides detailed descriptions on system functionality and explains all features and tools available to the user.
Users
OS6 provides three user access levels to cater for a variety of roles and are described as follows:
| User Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Light User | Read-only access to the system. This account has no functionality that allows the user to do anything other than view the system |
| User | Regular access for monitoring the system. Can acknowledge system alerts but cannot make changes to the configuration. |
| Trained User | Designed for system administrators. Provides further tools and abilities over the regular user. |
| Super User | Engineer-level access that is protected by a TOTP code. Allows system configuration and tuning. |
This manual primarily provides guidance for those with User-level access. However, it is also applicable to Light Users, but in a view-only capacity.
Additional modular manuals are available for Trained Users. For further details on manuals or a particular installation, please contact a Luna representative.
What is Luna OS6?
OS6 is a Luna's sixth-generation, fibre optic based asset monitoring system. It provides surveillance of the acoustic activity at any point along a deployment of fibre optic cable, which is partnered with sophisticated detection algorithms to provide automatic event alerts to the end user. These alerts provide a powerful, automated means of monitoring linear assets such as perimeters, borders and pipelines, alerting the user to the presence of unauthorised activity taking place.
Navigating the GUI
This section explains in detail how to navigate around the GUI and describes the functions available to the user.
GUI Overview
The typical User GUI display arrangement will include two main features:
- Main Map Window
- Surveillance Waterfall
The layout of these features is highly customisable and extra tools may be available dependent upon client requirements.
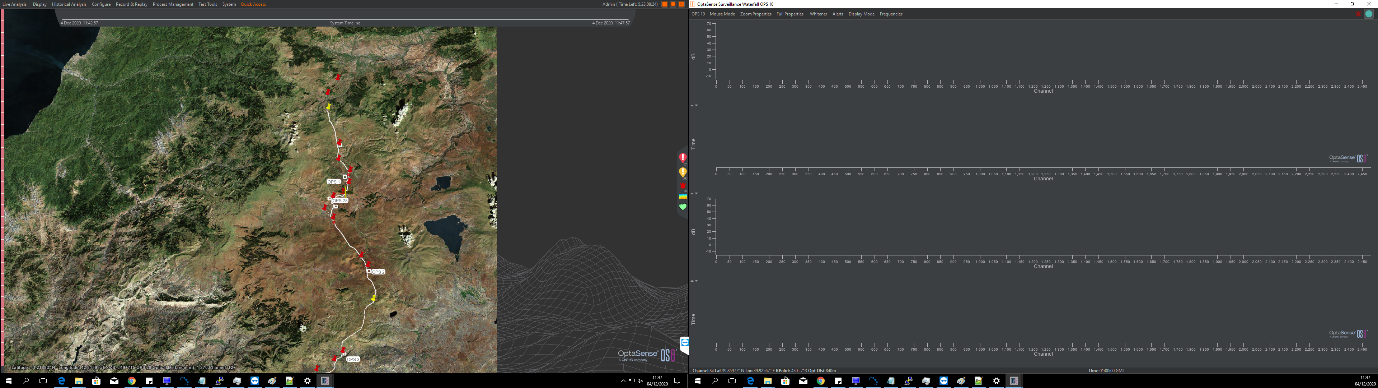
Main Map Window
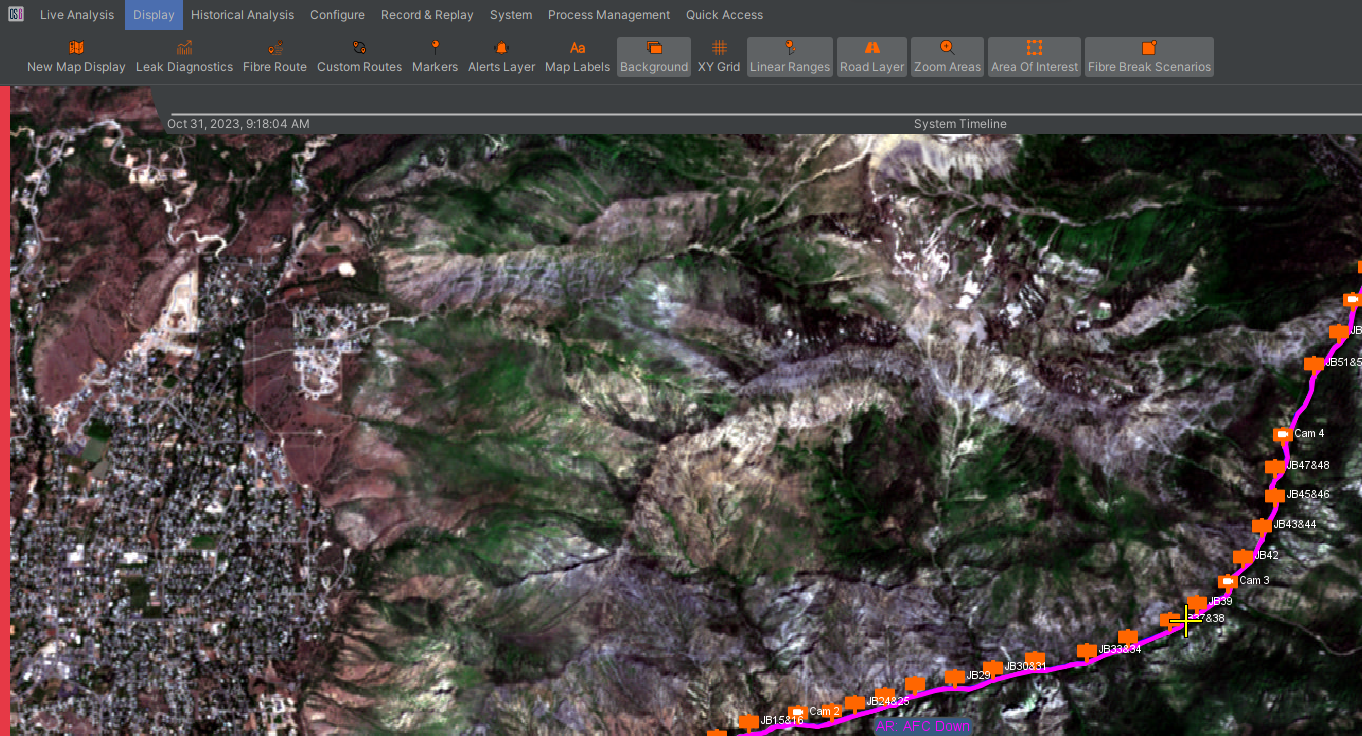
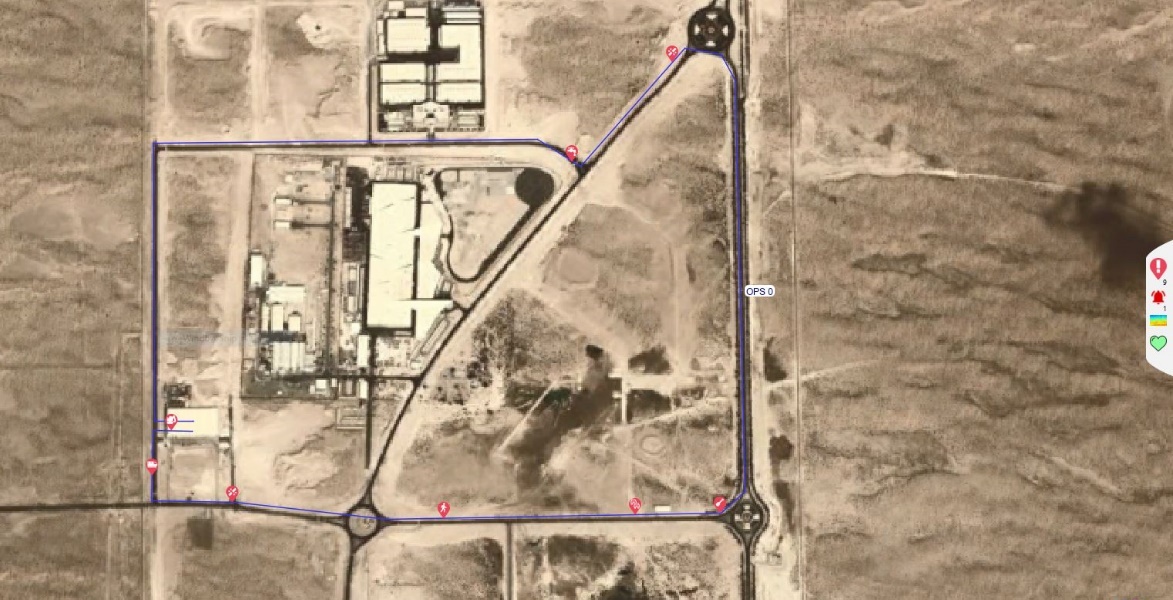
The map window is the primary interface for displaying alerts in real time on a geographic representation of the asset. A large amount of information is available in this window, including the fibre route, map imagery, zones, alerts, path layers and markers.
The map window (shown below) consists of several key elements: The map itself, menu options to access other system functions, the system health bar, the side status bar, the system timeline, and the toolkit. Each of these provides access to functions that are used to monitor alerts, navigate the map and to associate alerts with their locations on the map.
The Menu
The menu bar provides access to all the functions that a User requires. Users with lower access levels will have reduced functions available.
![]()
Described below are the default features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Live Analysis | |
| Provides access to: | Alert / Pre-Alert list - see LINK Waterfall - see LINK Analysis - Opens the signal analyis tool Frequency Analysis - Opens the spectral analysis tool |
| Display | |
| Provides access to: | New Map Display – Opens an additional map display. Markers – Allows the user to toggle markers on and off. Imagery – Toggle imagery layer visibility. XY Grid – Toggles the XY Grid visibility. Paths – Toggles the path layer visibility. Alerts Layer (Map Only) – Toggles whether alerts are displayed on the map. This does not stop alerts appearing in the side status bar or on the system timeline. Fibre Break Scenarios - Controls whether Fibre Break scenarios are displayed on the map. This does not prevent alerts or errors displaying in the side status bar or system timeline. Custom Routes – Toggles custom scale layer visibility. Area Of Interest – Turns on and off the real time areas of interest on the map. This does not stop them functioning. |
| Historical Analysis | |
| This provides access to: | Alert History Waterfall – see LINK. Multi-Channel Analysis – see LINK. Historical Alerts – see LINK. Historical Timeline – see LINK. Historical Process Metrics – see LINK. |
| System | |
| Provides access to: | Look and Feel - Allows the user to change the colour scheme of the GUI. Config management – Allows the user to import & export a system configuration. Alerts - Allows the user to acknowledge and dismiss Alerts. Save User Profile - Allows user to save current display/profile. Logout – Log out the software for the next user. About – Show details about the system. Quit the User Interface – Log out the software and close the GUI. Report Issue – Allows the User to create a support ticket that can be sent to Luna. |
The Map Display
The map is the core of the main display and typically comprises in the form of satellite imagery of the asset being monitored. Alternatively, it could be a schematic or any other image file depending on customer requirements. For the purposes of this manual, the map layer is satellite imagery and is geo-located using the data provided by the map provider (i.e., the cursor position on the map relates to the latitude/longitude coordinates of that position). Information on the position of the cursor on the map is displayed along the bottom of the map window. This readout also includes the cursor coordinates, OPS number, Optical Distance, point number and custom spatial reference. This might be a Kilometre Point (KP) and segment name.
![]()
Toolkit: General

The toolkit is one of the main access points for interacting with the map display. From the top row of the toolkit, the user can:
- Pan: Select to move around the map.
- Ruler: Select to measure the distance between two points on the map.
- Bounded Historical Search: Select to open a Historic Waterfall/Alert search for an area bounded as drawn on the map.
- Zoom In / Out: Click to zoom in or out of the map.
- Reset: Click to return the map to the default position.
- Map Cursor: Clicakable options to decide how the map cursor and position should behave when focusing on or tracking alerts.
Toolkit: Alerts
Additional options are available from the toolkit that can be used to interact with selected alert(s):
- Acknowledge/Dismiss: Acknowledge or dismiss the selected alert(s).
- Alert Comment: Add a comment to the selected alert(s).
- Alert Details: View additional information about a selected alert within the toolkit.
- Waterfall Preview: View the historical waterfall associated with a selected alert.
- Multi-Channel Trending Preview: View data trending for a selected alert.
- Historical Waterfall: Open the historic waterfall display for a selected alert.
Alerts can be selected by:
- Map: Clicing on an alert on the map. The selected alert will be highlited by a dashed rectangle.
- Alert Right Click Menu: Click the "Select" option
- Alert Table: Highlight one of more alerts by selecting them in the alert table.
Map Right Click
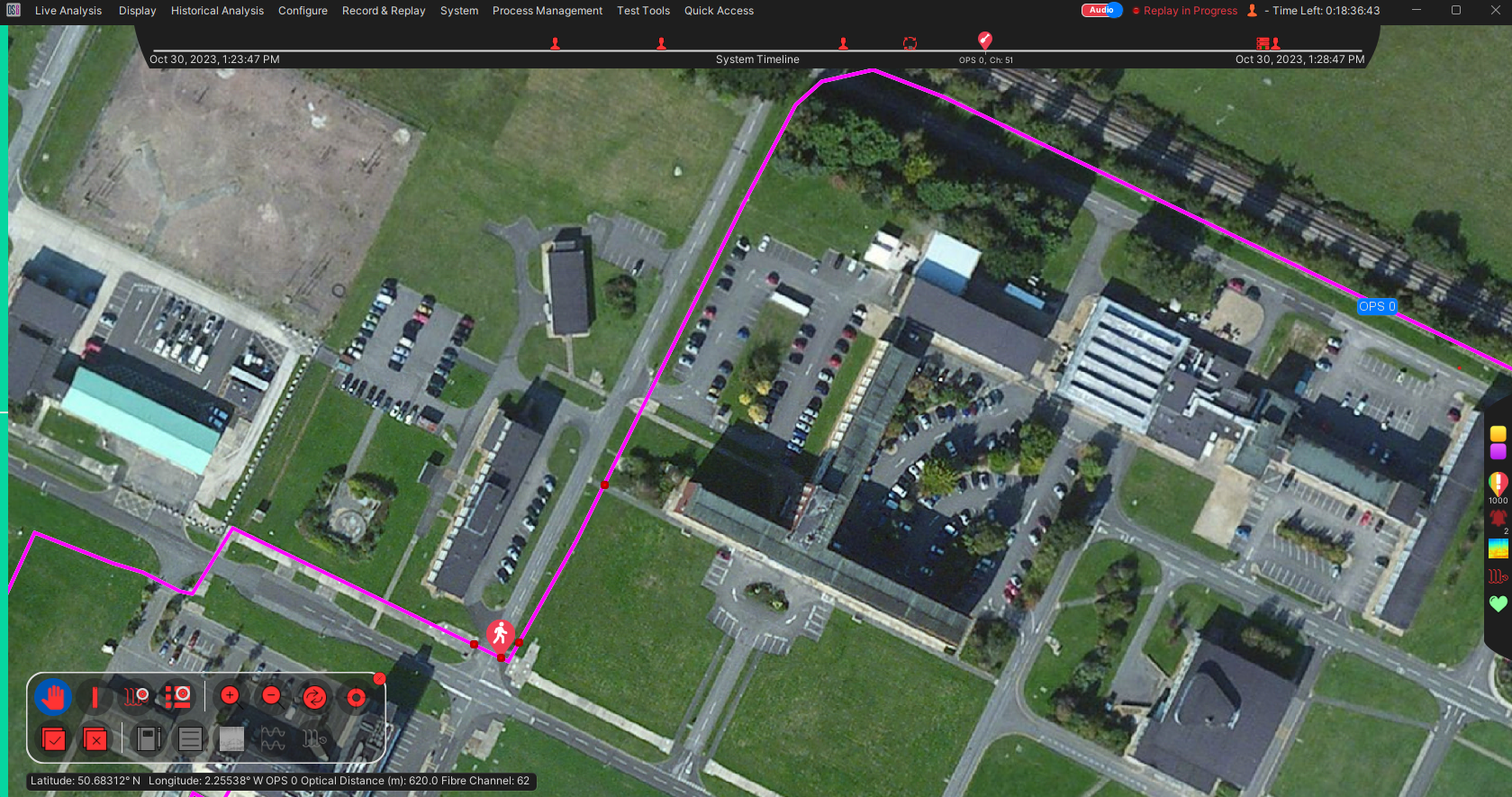
Right clicking on the map will open a window with several navigation options and are shown below. These options will vary depending upon user type and where the user clicks on the map. For example, clicking on the map alone will give the user a different set of options to when they click on alert or a marker.
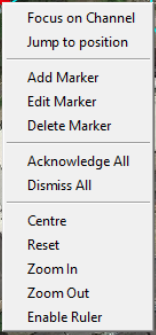 |  | |
|---|---|---|
| (a) Right click on map alone | (b) Right click on a marker icon | (c) Right click on an alert icon |
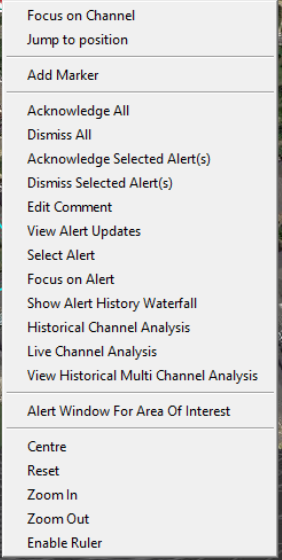
Focus on Alert
 This will move the highlight marker on the waterfall and focus on the alert nearest to the cursor on the map window. If this function is selected from the alert list (detailed in Section LINK??) it will focus on the selected alert.
This will move the highlight marker on the waterfall and focus on the alert nearest to the cursor on the map window. If this function is selected from the alert list (detailed in Section LINK??) it will focus on the selected alert.
Focus on Position
This will do the same as “Focus on Alert” but will bring up the waterfall and centre it on an area around the position selected.
Move Map Cursor
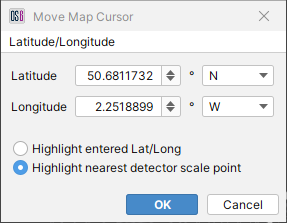
Select this to highlight a specified latitude/longitude or the nearest scale point to it. A cross will appear at the specified location on the map.
Configure Markers - This option is not available to regular users, so remove?
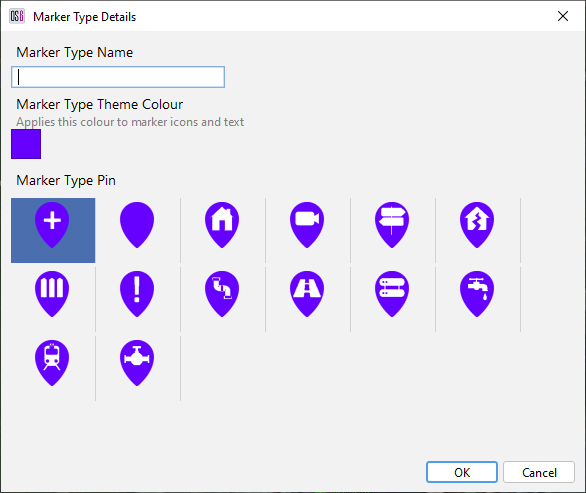
OS6 has several pre-defined marker types that can be implemented on the display. To add markers, select the ‘Configure Marker’ Tab on the Map.
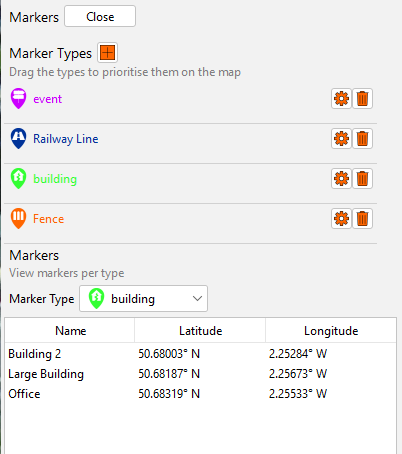
To configure a Marker Type, press the ‘+’ button. The Operator is presented with a set of pre-defined icons. The Operator can select one of these and assign a Marker Type Name and colour.
This Marker Type can then be used to create a Marker on the Map.
Add/Edit/Delete Marker - This option is not available to regular users, so remove?
To create a marker, right click on the map where the marker is required, then click “Add Marker”. A pop-up window will appear asking for a name and marker type. Note for “type”, there will only be one selectable option. For information on how to add another type, refer to Module 6 - Configuration Wizard User Manual, Section 3. To place a marker at a specific location, change the coordinates after clicking “Add Marker”, then click “OK”.


Markers can be edited by right clicking on them and selecting “Edit Marker”. The user will then be provided with an option to edit information on the selected marker. Once the desired modifications are made, click “OK” to save changes.
To remove a marker, right click on the marker, and then click “Delete Marker”.
This part is available to regular Users
To refine how markers, appear on the map, select “Display” in the top left of the map window. Select the marker layer. The following options will appear in the top right of the map window.
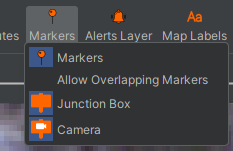
-
Markers – Turns all markers on or off.
-
Allow Overlapping Markers - Having this option unchecked refines how the markers are visually represented and can reduce clutter of the map window when several markers are close together.
-
Type X – Allows individual markers to be hidden or displayed.
Areas Of Interest
This feature can be useful if there is a region of activity which is causing many alerts and the cause of these alerts is known, for example, pipeline maintenance. The Area of Interest is configured by Administrator level users and above, however they are visible to the User, who can view the alert lists for these areas. They can be viewed by right clicking on the area and selecting Alert Window for ‘Area Of Interest’.
Once this is selected the Alert list for the area is displayed and the user can acknowledge and dismiss alerts for that area as well as carry out the functions as described in Section Link??.
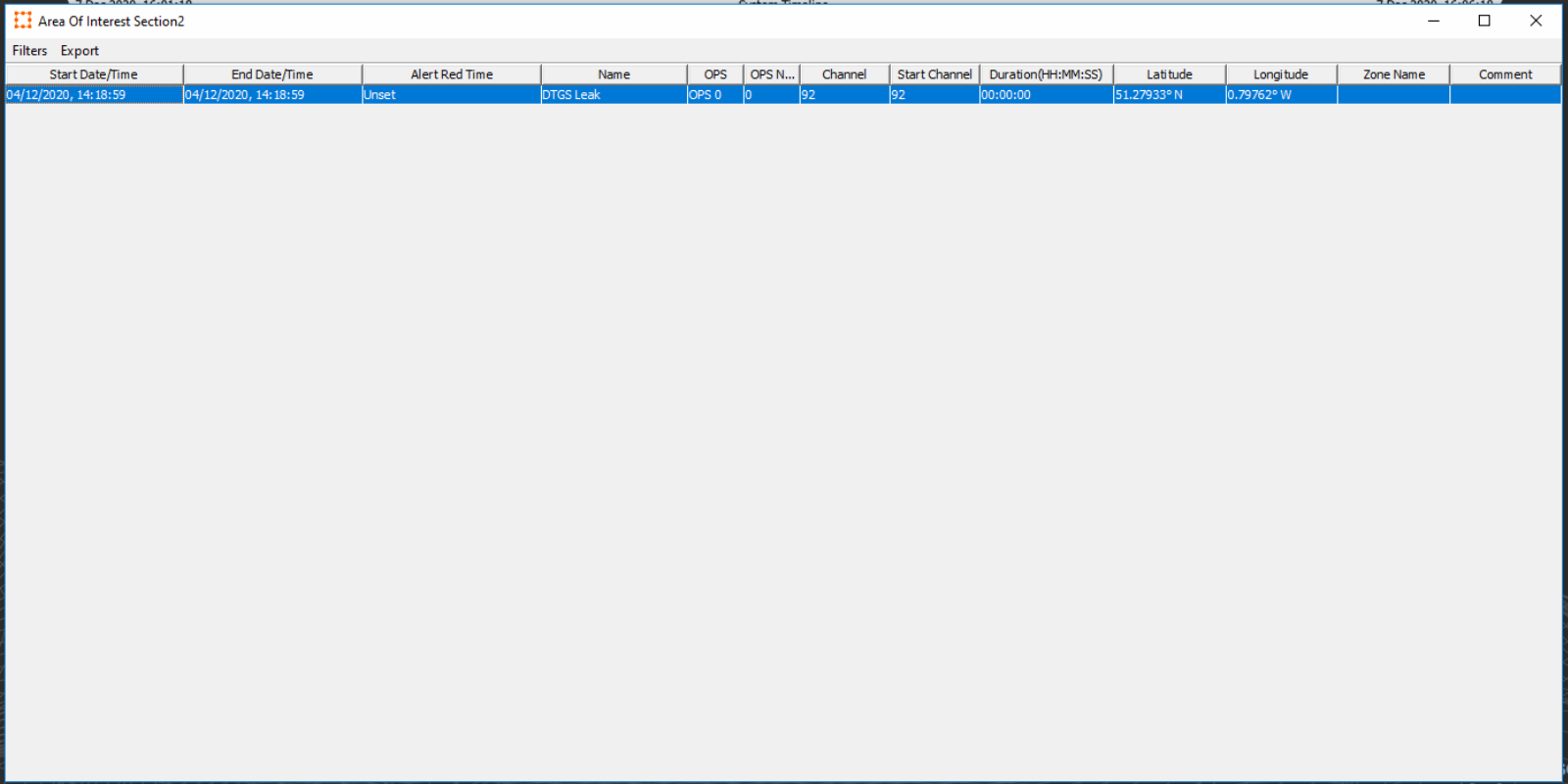
The window also allows the user to filter and export alerts.
Map Layers
Map layers provide different functionality and information on the asset. Layer visibility can be controlled from the Display Menu.
Many of the layers have configurable options to refine the information that is displayed on the map.
| Map Features | |
|---|---|
 | Fibre and Custom Routes The fibre route and any custom routes are represented by coloured lines on the map display. |
 | Markers Points of interest can be marked on the map using markers. Different marker types can be enabled/disabled independently as well as the entire marker layer. An option for whether to allow overlapping markers is also available. |
 | Alerts Current alerts are shown as an icon displaying the type of alert. The alert icon size can be configured between two sizes. After the activity is finished and 5 minutes has passed, alerts will fade to a red dot on the map until the alert is dismissed from the alert table |
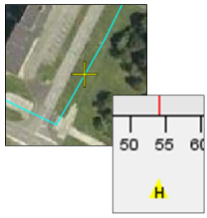 | Channel Highlight This marker is an important link between the map window and the waterfall. A "focused" channel will be highlighted by a line on the waterfall and a yellow cross will indicate the corresponding location on the map. |
Real Time alerts will appear on the map as they happen.
Geographical Alert / Waterfall History Search
Alert History Search
To perform a search for alerts in a specified area on the map window, select “Open Bounded Historical Alerts” from the map Toolkit.
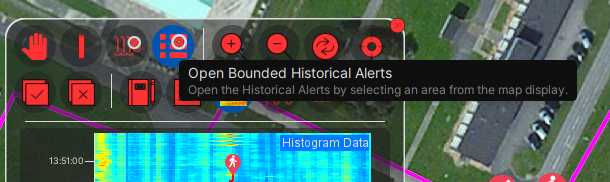
Once selected on the Toolkit, draw a box around the area on the map to be analysed. When the mouse is released, the historical alerts search window will be displayed with the channel range already defined based on the window that was drawn.
Historic Waterfall Search
Similarly, a historic waterfall for a specified area can be created by selecting the Bounded Historical Waterfall option from the map toolkit. Once selected, draw a box around the area on the map that requires analysis. The waterfall search window will open with the specified area.
Side Panel
The side panel is accessible on the right-hand side of the map window and can be expanded to show several different displays. These include:
- Alerts Overview
- System Notifications
- Quick-view waterfall
- System Health Overview
- Historic Alert Waterfall In addition to these options, there is a split panel that allows the user to display two of the available displays simultaneously ina vertical stack.
Alert Overview
The alert overview is displayed on the right side of the map window within the side status bar. To access, select the multi-colour alert symbol on the side status bar will slide out. The alert panel shows all current alerts on the system and can be quick filtered by alert level using the buttons at the top of the window. Further filtering options are available from the funnel icon at the top-right of the alert panel. Alerts that have been dismissed will not be visible, but these can still be accessed through the Historic Alerts tool.
Selecting an alert will highlight the alert. The details of that alert are then displayed below in an alert summary at the bottom of the panel.
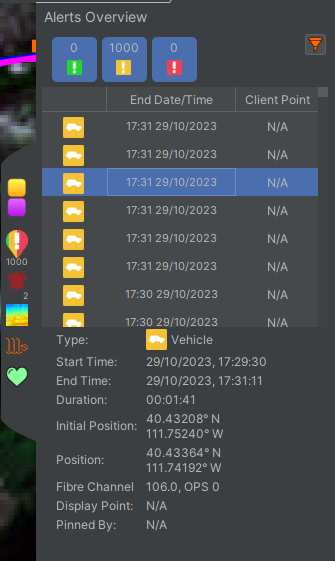
The headers that are displayed in the alert table can be configured according to user preference. Additional headers are available by right-clicking on the header row. The alerts that are displayed in the table can be sorted according to the available headers by clicking on the respective header.
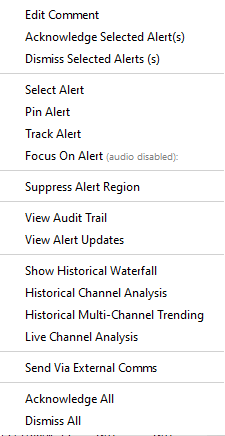
Each alert also has a context menu accessed through the right-click action that provides further alert specific functionality.
Acknowledged alerts will remain in the alert overview panel with the alert colour greyed out.
Side Waterfall
A further option that is available to the User is the Side/Quick View waterfall. This is accessed by clicking the waterfall logo on the sidebar.
 | |
|---|---|
| (a) Side waterfall opening logo | (b) Side Waterfall |
The Side panel waterfall has some of the common functionality of the full waterfall. These can be accessed by right clicking on the window.
| Reset Zoom | The Side waterfall allows the user to zoom in, in the same way as the full waterfall. This allows the User to rest this zoom |
| Properties | This allows access to the functions described in 6.4.7 and 6.4.8 |
| OPS X | Allows the user to change the OPS being displayed on the side waterfall |
| Rate | Allows the User to adjust the update rate of the waterfall |
| Display mode | Allows the User to toggle between the configured modes |
System Summary Overview
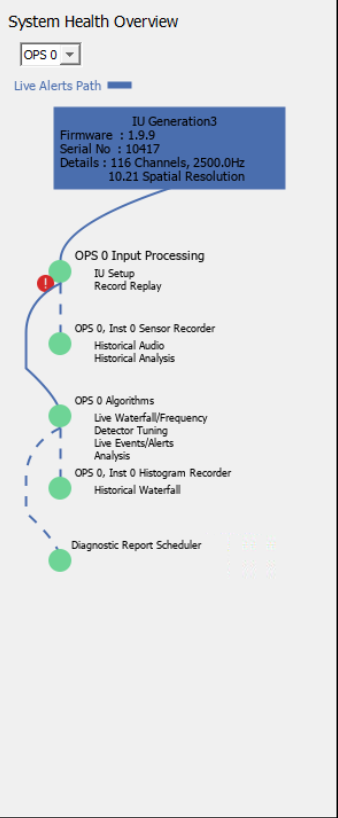
Select the green heart to access the system summary overview. This panel shows the system health and gives a graphical representation of the system processing chain with information relating to the selected OPS. As the data is received by the interrogator unit it flows downstream through the processes represented by the green circles. If any of the processes are in an error state it will be reflected in the display.
System Timeline
The system timeline is a means of gaining a quick overview of what is happening on a system.

The system timeline is a rolling timeline with the period of coverage displayed on the left- and right-hand sides. When an event occurs, a symbol appears on the timeline to indicate the type of event. This can be clicked to provide further information. Examples of when an alert is selected and when a system event is selected are shown below.
Some events will also include subtext. For example, alerts scrolling across the timeline will highlight their centre position.
Surveillance Waterfall Window
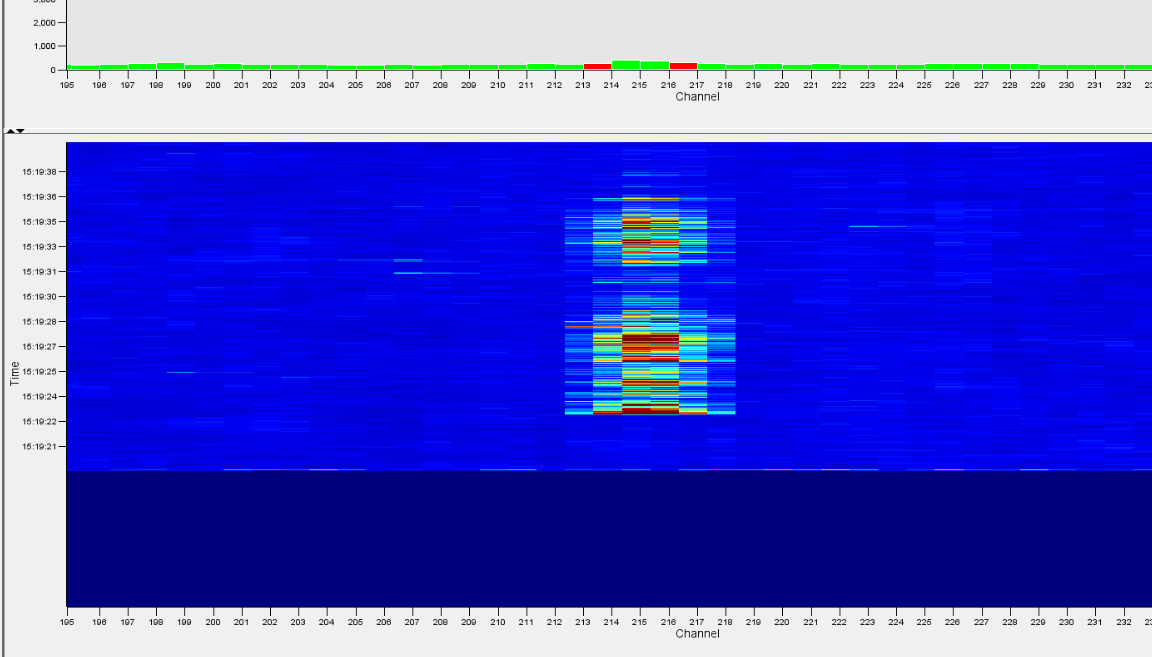
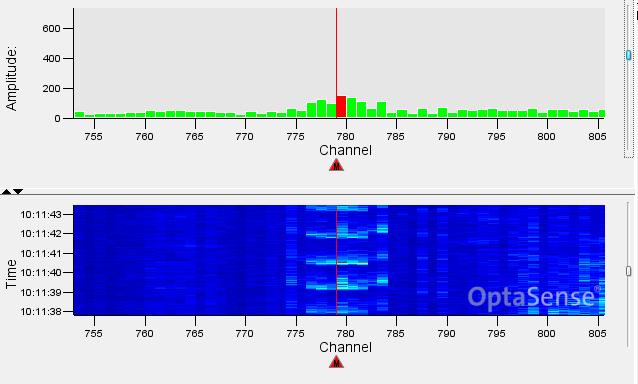
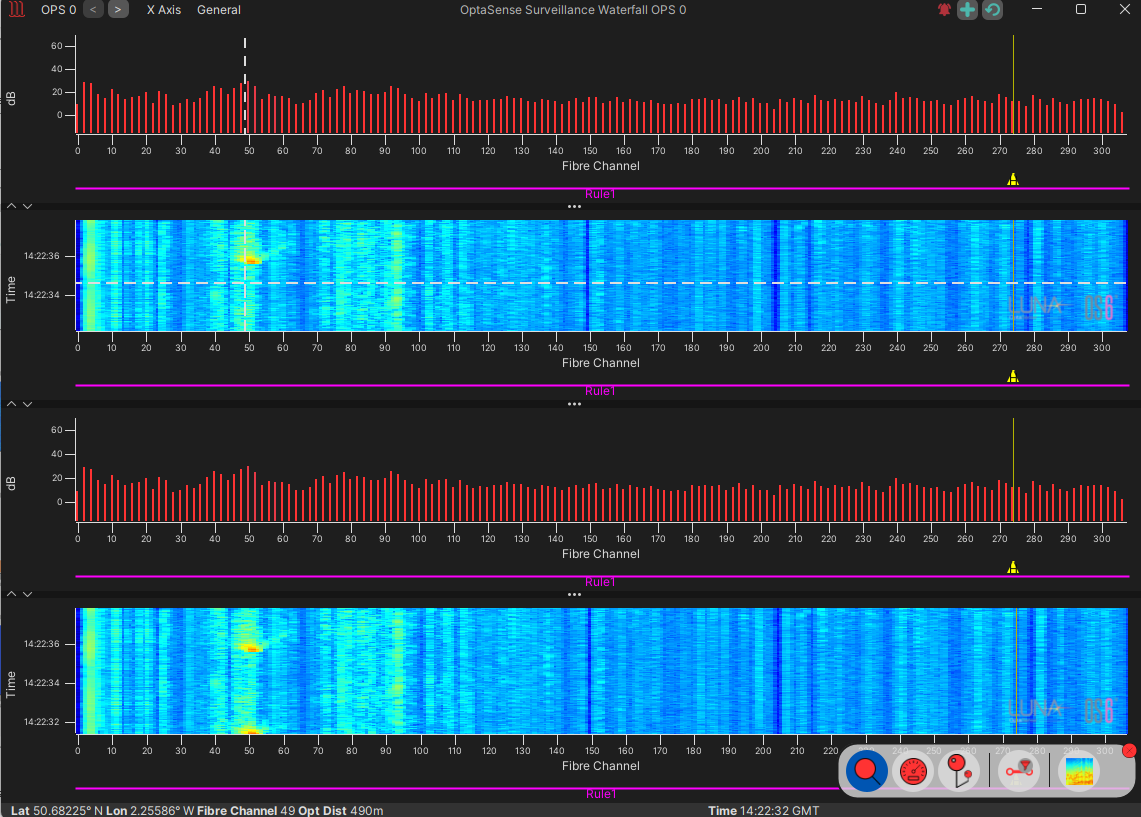
The surveillance waterfall window displays sensor data along the entire length of the sensing fibre. The data is displayed with time on the vertical axis and a representation of fibre location along the horizontal axis.
The surveillance waterfall has two main types of charts: waterfalls and histograms. The default arrangement consists of two panels with the upper panel being a zoomable waterfall while the lower panel will always display the full fibre route across a single system.
Each display on the waterfall window can be adjusted to enlarge or shrink the different components by clicking and dragging the borders of each section. Components can also be minimised and maximised using the arrows on the borders.
Waterfall Toolkit
The waterfall toolkit provides easy access to many of the commonly used controls. The toolkit can be minimized by clicking the x in the top-right corner and re-opened by clicking the toolkit icon itself (visible when closed).
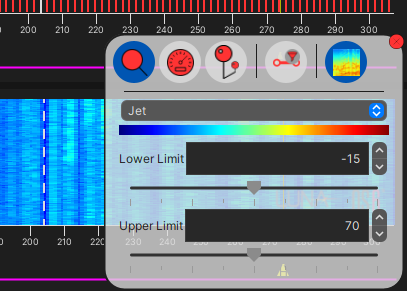
- Scaling: The gain levels can be adjusted using the horizontal slider below the scale limit – or by typing in numbers directly into the box. This will affect the histogram displays and the colour scaling on the waterfall displays.
- Mouse Mode:
- Zoom – Allows the user to magnify sections of the waterfall to see the data with greater resolution.
- Create Linear Range/ Detector Area – Allows the user to create new areas by clicking and dragging on the waterfall display. This functionality is only available to higher-level users.
- Measure Speed – Allows the user to draw lines on the waterfall display to determine the speed at which a signal is moving. The units can be selected from the sub-menu.
- Range Coverage: Control what is shown beneath the histogram and waterfall charts: e.g., Linear Ranges, Detector Areas. See Figure 41.
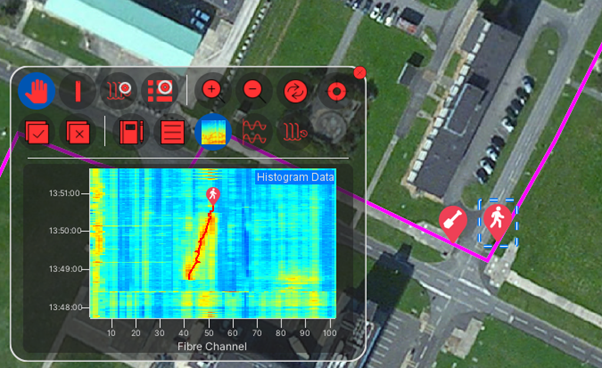
Histogram displays
The histogram displays show live data along a a fibre route with the amplitude of the signal shown on the vertical axis.
A red bar indicates that there is an unacknowledge alert at a given location.
Surveillance Waterfall
The waterfall charts display the recent history of the signals detected on the system. The horizontal axis agains represents the location along the fibre. However, the vertical axis now represents time, and the colour of the data indicating the signal amplitude. In the default scheme (Jet), lower amplitude signals are blue higher amplitude signals are red. Many colour schemes are available and this can be modified according to user preferences.
The amount of data on the display can be configured through the right-click menu. A rate of 1:1 will display the least amount of historic data while the most is displayed with a rate selection of 1:64. Different events are easier to visualise over different timeframes. For instance, a person walking will be most clearly visible over a short timeframe while the movement of vehicles can be easier to interpret over longer timeframes.
Note that the upper zoom window can be selected from all the individual panes – zoom and overview, waterfall, or histogram. It is important to note that the upper zoom views are always correlated; the user cannot select different zoom channels within the histogram and waterfall for example.
Optimising the Displays
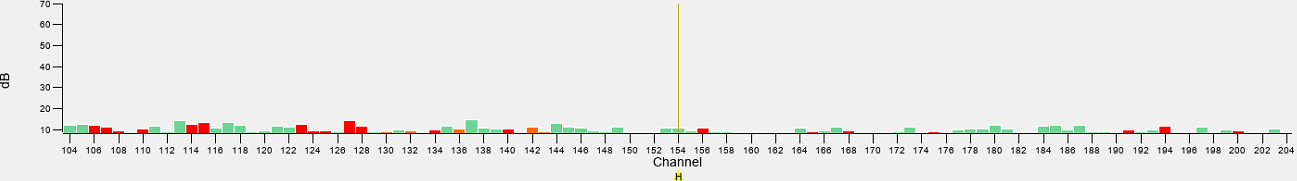 | Not Enough Gain – Some Very Strong signals are only just visible |
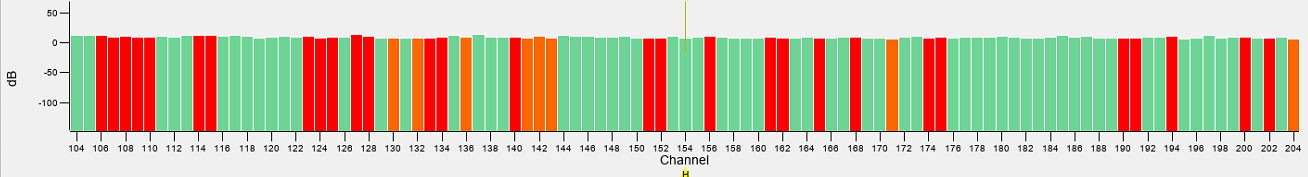 | Too Much Gain – Lots more data is visible but some data from early channels is extending above the range of display |
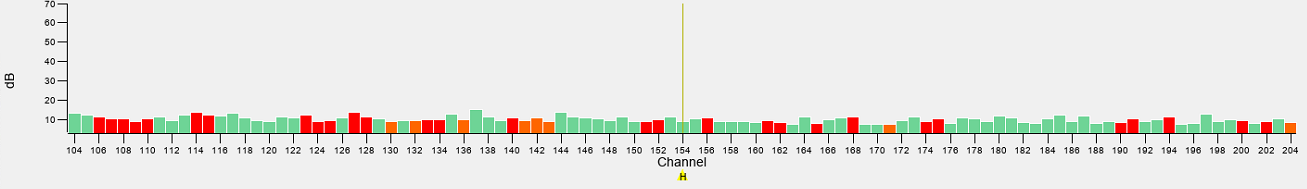 | Correct - full scale of all data is visible |
A method for selecting the optimal histogram magnification is to set the sliders within the range of the data being produced by the system. The default settings are a minimum of -15 dB and a maximum of 70 dB and each may need to be adjusted up or down according to each system. The widest scaling should be set so that the maximum signals observed will nearly hit the maximum amplitude limit and where the lowest signals are just about the minimum level. However, as much of the low signal is often background noise it can improve the data visualization by raising the minimum level slightly above this noise level. Similarly, it may be acceptable to allow the largest signals to become saturated so that that weaker signals are more pronounced against the background.
Some displays use the same data scaling and changes to one display will affect all others:
- Histogram
- Surveillance Waterfall
- Side Panel Surveillance Waterfall
Data scaling is unique to each OPS on the system and can be configured for each user as well.
Zoom Function
The histogram and waterfall displays are zoomable to focus in on activities that are taking place. To zoom in on the display, click and drag a box anywhere on any of the waterfall/histogram displays while the mouse functionality is set to zoom. All zoomable displays will zoom to this range. Note that the lower most displays will always show the full range of data with the current zoom range indicated on them.
Right-clicking on a zoomed display and selecting “Reset Zoom” will restore the display to show the entire fibre route.
Waterfall Functionality
Cursor Information
Details on the position of the cursor on both the waterfall and histogram charts will be visible at the bottom of the window. Information includes the channel, the Latitude and Longitude and the Optical Distance at the position of the cursor. If the system has a custom layer (such as KP for pipelines) then this information will also be displayed.
Menu Options
Across the top of the Surveillance Waterfall are various control Options for the waterfall
| OPS | Allows the User to select the OPS to be displayed. The arrows provide easy switching between OPS. | |
| General | Allows the user to toggle between whitened/non whitened data. Toggle on/off alert tracking on the waterfalls. Toggle the visibility of Zones/Areas. See Section 6.4.4 Can also React to a Focus Request Focus Alert Focus Position Track Alert | |
| X Axis |  | Allows the User to change the units of the horizontal scale. Any Detector Route (Asset, Fibre) or Client Scale available on the selected OPS can be used. |
Zones
The zones are represented across each of the displays on the surveillance waterfall. They correspond with the zones shown on the map display.
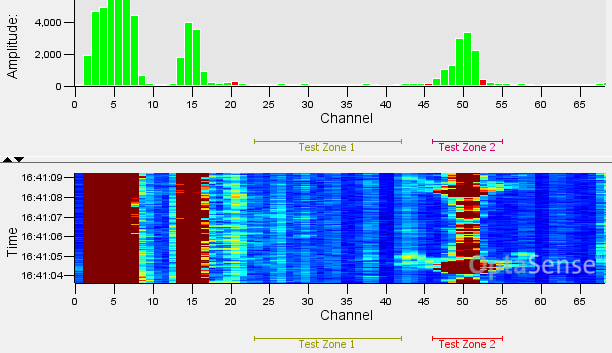
Channel Highlight
The channel highlighter is visible along the bottom axis of the waterfall and histogram charts. This indicates the currently selected channel that will be used in the channel analysis tool and where audio output will be delivered from if enabled.
Add an image??
Right click functions
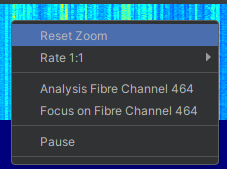
Both the histogram and the waterfall charts can be right clicked. The following options will be accessible:
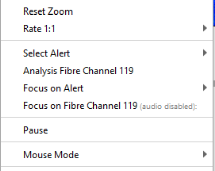
| Reset Zoom | This resets the zoom levels on both the overview and zoom waterfalls back to show the whole OPS |
| Rate | Determines the period of time that can be displayed on the waterfall. |
| Focus on Fibre Channel ‘X’ | ‘X’ refers to the point number where the mouse was clicked. The Map Display and Surveillance Waterfall will snap to centre the selected channel. Markers will be placed both on the histogram and the Map Display to highlight the channel. This also combines the Listen to channel function |
| Focus on Alert | This will focus and highlight both the map and waterfall onto the nearest alert to the position of the cursor. |
| Analysis Fibre Channel X | This will open an analysis window giving advanced audio information on the selected channel. Depending on the user level this option may or may not be available. |
Waterfall Colour
The colour scale for the waterfall can also be modified from the control panel, the system default is Jet. These can be selected according to operator preference.
The “Heat” and “C3” colour options have a lower dynamic range than the other options.
Linking to the Map Display
Data on the waterfall and histogram displays can be linked to the corresponding location on the map by right-clicking on the chart and selecting “Focus on Channel X”. The zoom chart will then focus on the selected location and the yellow cross will be displayed at that same location on the map display. This also works in reverse by right-clicking on the map window to select a specific location and have the zoom charts focus on it..
Additional Functionality
Alert Window
The Alert List Window will display all active alerts from the system. It acts in a very similar way to the alert window on the map window but has greater functionality. The alert window is accessed within the main toolbar under live analysis. It shows greater information about each alert.
Similar to the Map display, there is an associated Toolkit, that allows easy access to the most common actions
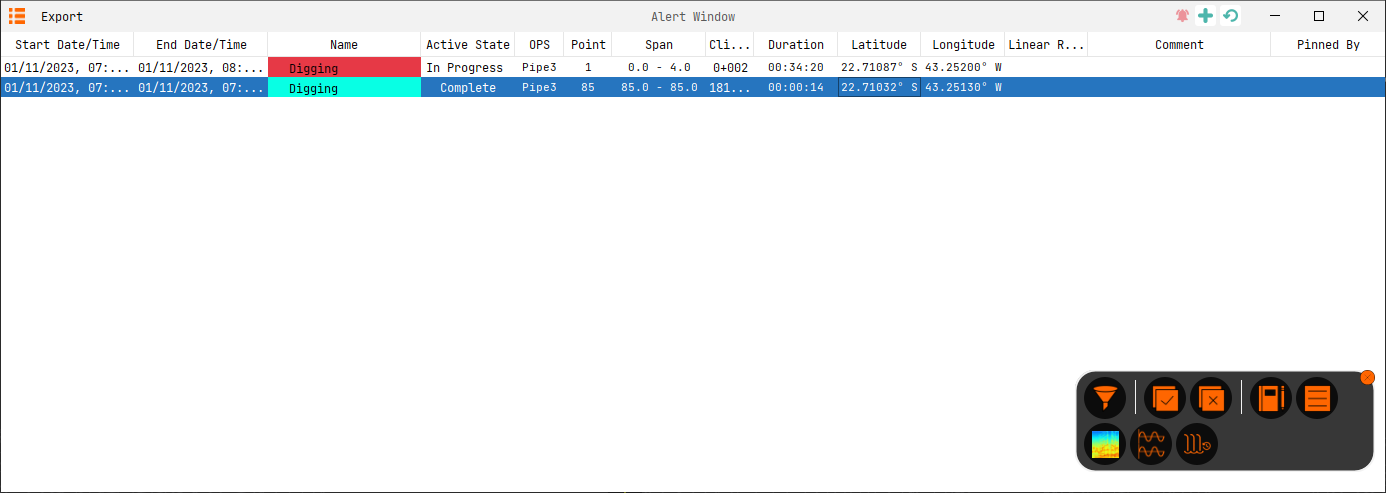
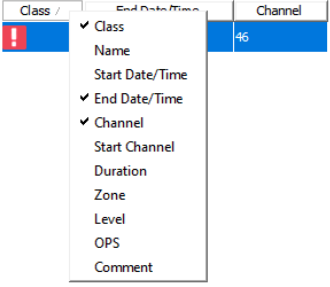
The visible headers can also be customised by right-clicking on a header to get a list of available headers. Click on a header to then sort by ascending/descending order. It is also possible to filter against any available headers.
The ordering and choice of columns can be stored when saving current view as user profile.
Audio Control Window
| The Audio Control Window provides the user with a variety of tools to modify the audio settings on the system. Once clicked, it will open a simple volume fader which controls the master volume of the system. If set too high the audio may distort and the “Out of Range” light will light up. If this occurs, turn down this slider until the light is no longer on. | |
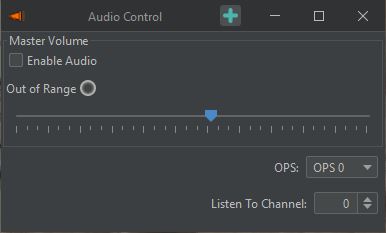 | Master Volume Controls the volume of the system created sounds. Enable Audio This acts as a “mute button” for audio data. If this is unchecked, no sound will be observable from any channel of the system. Jump to newest Alert The audio will be played from the channel of the latest alert. If this alert updates to a different channel, or a new alert begins, the audio channel will automatically switch to the newest update. |
The Audio status is available on the main GUI toolbar where it can be enabled/disabled.
Recording and Replaying Data
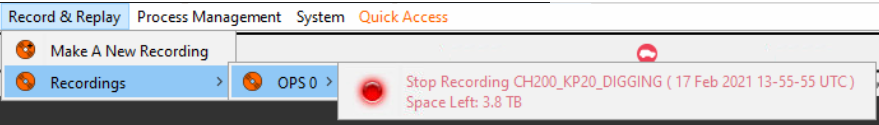
The system can record and replay data. The functionality is restricted based on user level with only Trained Users being able to replay data. Light Users are unable to record or replay data. If this has been enabled, then the button will be visible on the toolbar. Selecting the “Make a new Recording” button from the Record & Replay tab on the main toolbar will bring up the window shown below.
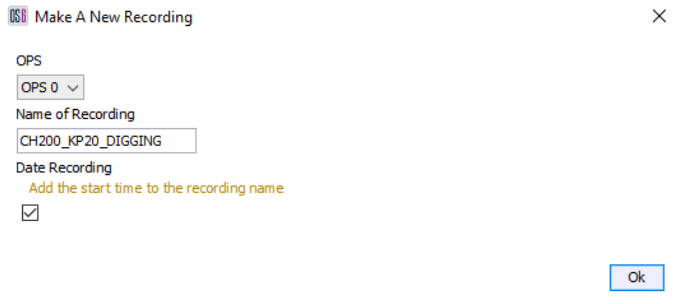
Recording
Before a recording is made it’s important to select which OPS the activity is going to be recorded from, it’s important to choose a suitable name so that it provides a good reference to what’s going to be recorded. For example, the Channel/KP point and type of activity.
Once the name is provided and OK is selected, the recording will begin. The dialogue box will disappear, and an indication will appear to indicate that a recording is in progress. Clicking this shows more detail. The sidebar can be used to stop the recording.
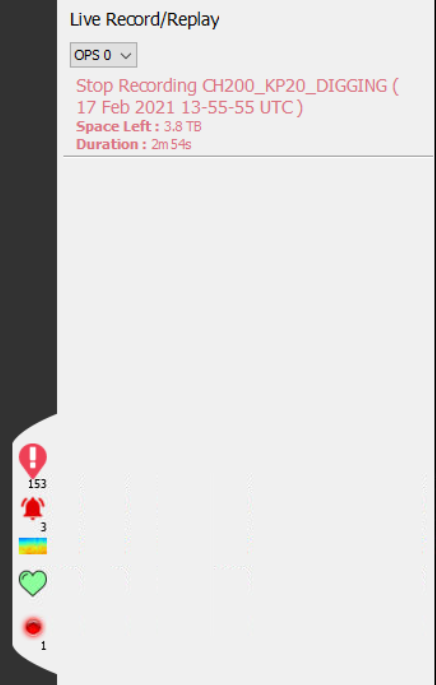
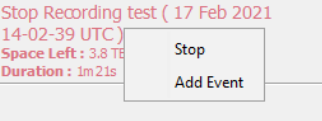
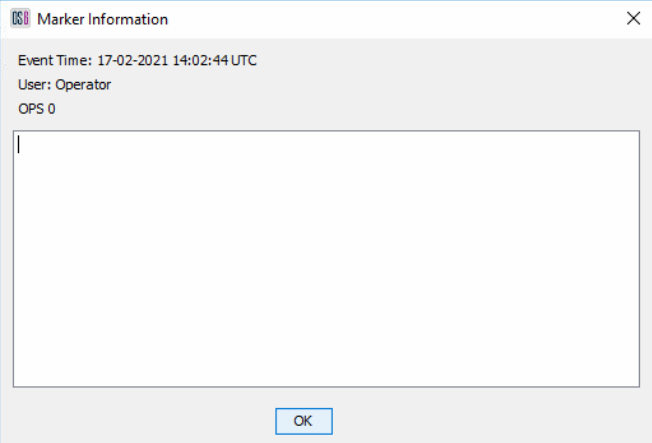
Whilst recording there is an option to log manual events. Logging an event provides a reference point within the recording to note where an event of interest happened. To mark an event, select the Add Event button, accessed by right clicking the recording in the sidebar This will bring up the box where a description of the event can be added. Selecting OK will place the marker.
User Profiles
Profiles allow Users to arrange the customise their display and then save that arrangement so that it can be recalled at any time, including when logging on to the system. The procedure for setting up a profile is detailed below.
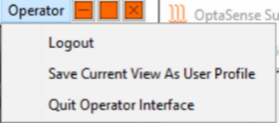 | Click on the Username (in this case User) in the top right corner of the Map window and selecting the option to Save Current View as User Profile |
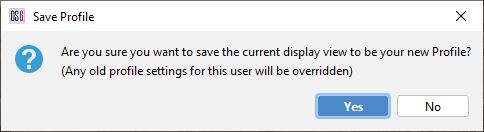 | Confirm you wish to save this view by pressing yes |
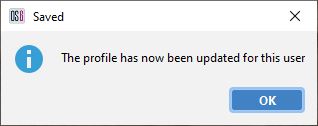 | Confirmation the save has been made |
| Once a profile has been saved, the layout will be loaded each time that profile is logged into. |
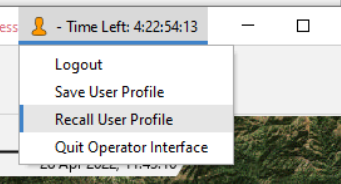
Recall Profile
If there is a profile for a user, this profile can be recalled by selecting "Recall User Profile" from the user menu. This will close any open displays and re-apply the saved profile.
Restore Defaults
Where users have made layout and visualisation changes it is possible to restore the window to the default settings by pressing the Restore Defaults () button. The button can be found in the top right of the window. Pressing this button will restore visual settings to defaults but will not make any changes that affect the underlying processing of the system. For example, the dynamic range of the charts will be reset but any changes to the frequency band of interest will not.

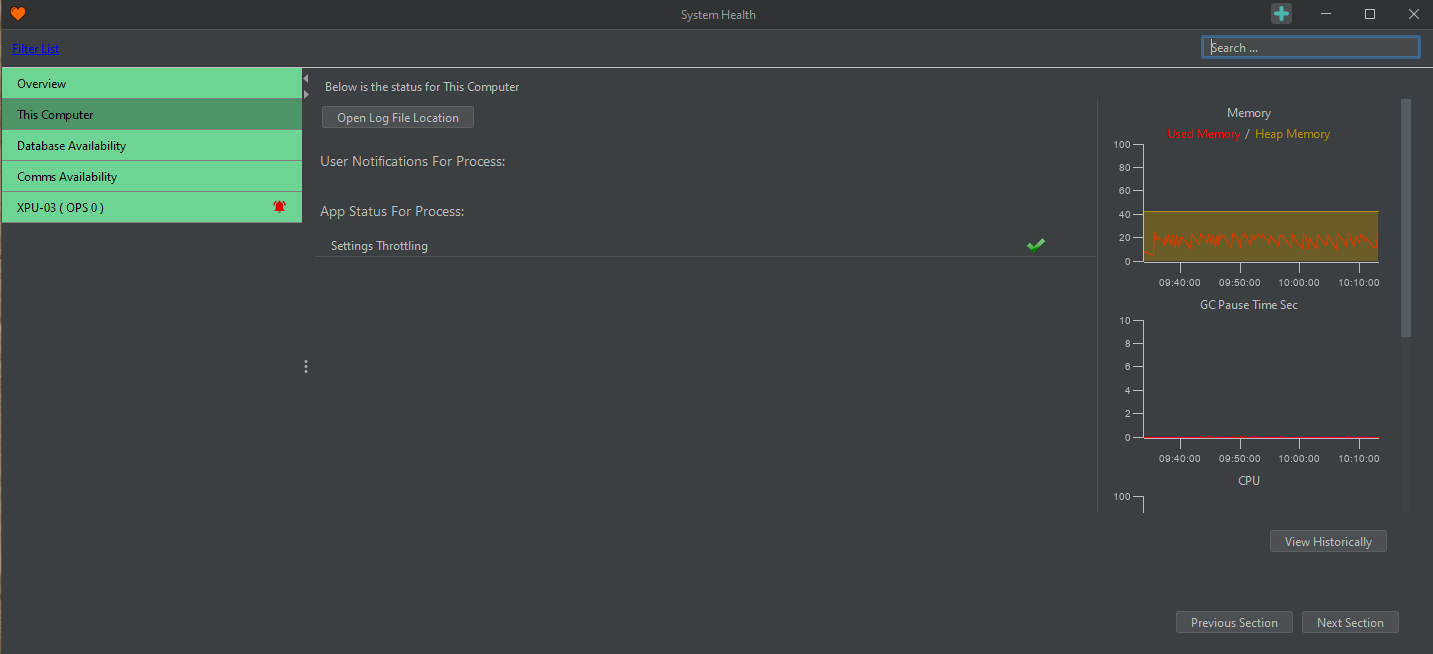
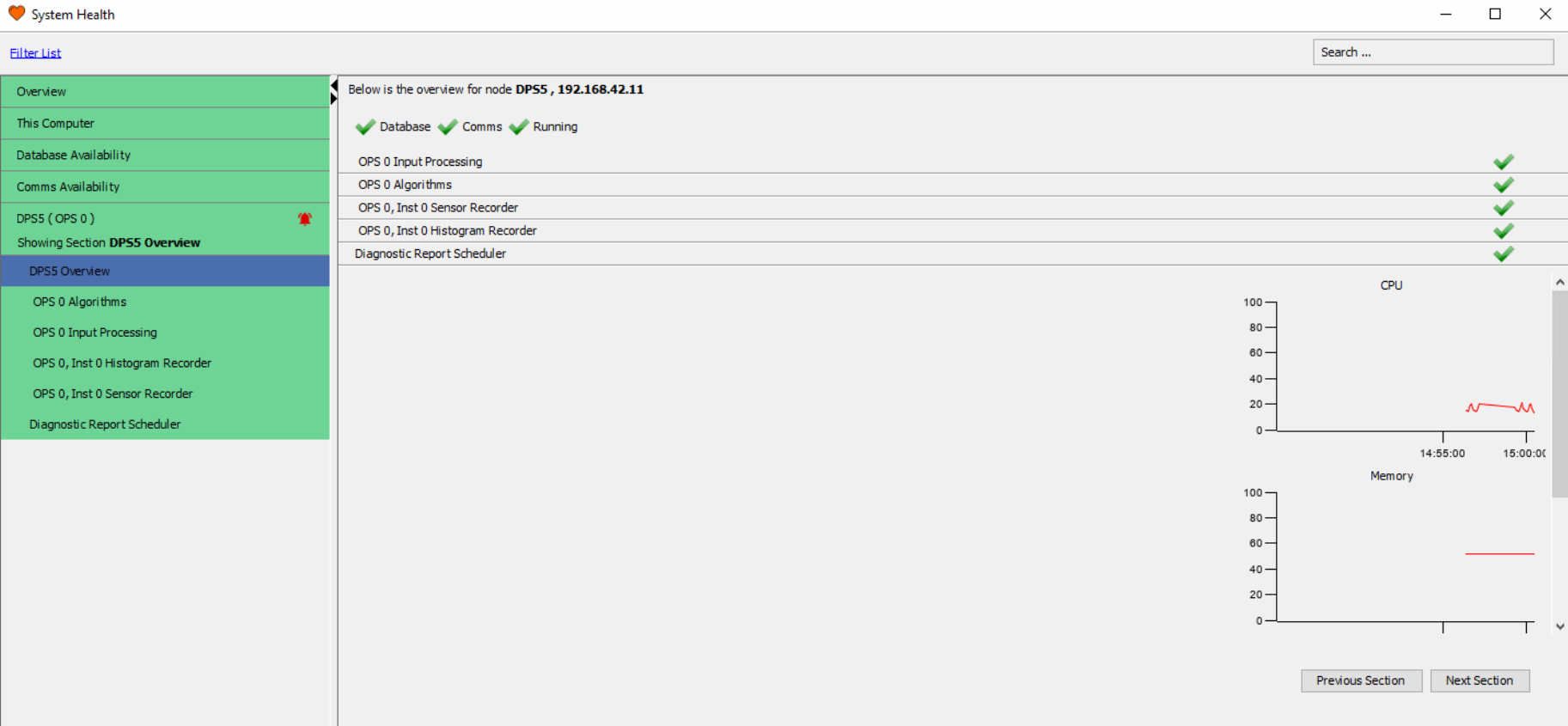
System Health
The system health window can be accessed by clicking on the System on the main menu bar.
This window provides information on all components of the system, both hardware and software. Within each window there are graphs which show a variety of different diagnostics:
By clicking “Filter List” in the top left, only Processing Nodes with errors are shown. This is very useful when operating a large system.
System Health on Map Window
The System Health light on the left-hand side toolbar will focus the User’s attention to any potential error messages or warnings.
![]()
Database and Comms Availability
This section details the connection state of the distributed database across the system.
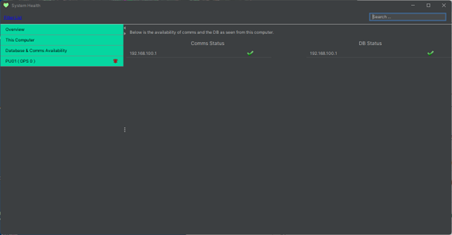
Node Status Overviews
The number of sections after the local logs section is dictated by the number of nodes processing units or dual processing units the system comprises. Each section can be expanded by clicking the banner.
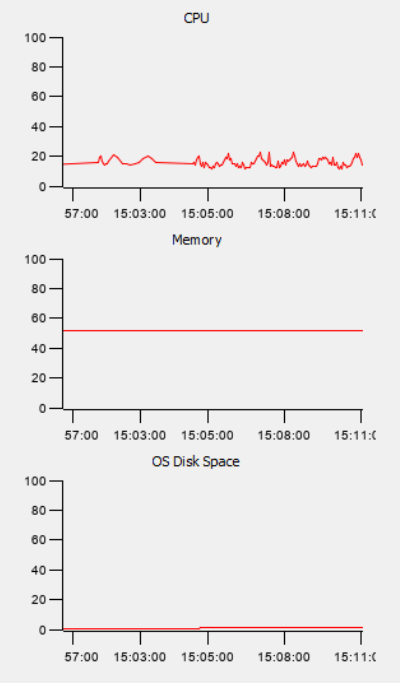
Resource Monitoring
On the right-hand side of the System Health window there are charts that provide an overview of status of resources. Process report charting enables the user to select what resources they want to monitor. Resource monitors include:
- CPU %: This is the demand on system processing. The higher the red line, the harder the CPU is working to service the system.
- Memory %: This shows the systems demand on memory. The higher the red line the more the system is using.
- OS Disk Space: This depicts how much of the drive on the server is being used.
Alert Management
Once the system has been installed and tuned, alerts will appear in response to the correct stimulus and may need to be investigated. Of crucial importance is the need to understand that the alert that appears may not identify malignant behaviour – rather it identifies behaviour that aligns with the type of alerts detailed within the threat profile. Correct use of the tools allows the user to observe and review the data in a timely manner allowing a full alert to be declared only when there is sufficient evidence built up to warrant a response.
As Users become familiar with typical behaviour that is observed along the asset, they will quickly learn to differentiate interesting behaviour from the mundane. Most typical linear assets will produce a few alerts per week – but this depends wholly on the nature of the background – for example, in areas of arable farming where digging is considered a threat, the number of digging alerts will likely be considerably higher than in a remote, unfarmed area.
How Alerts Appear
Alerts will appear on the map window as icons that indicate the location along the fibre and the type of alert.

Various alert icons are available to indicate examples of different activities: (from left to right) Activity, Leak, Mechanical Digging, Personnel, Pig Tracking, Train, Hot Tapping, Vehicle, Manual Digging, Landslide Detector, Seismic Activity Fibre break and Fence Activity.
A corresponding line of information will be displayed on the alert list to the right of the map if the alert is red.
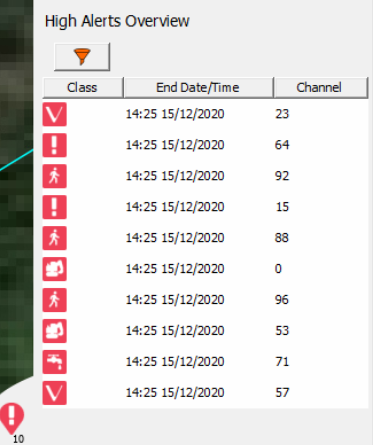
Dealing with Alerts
Alerts can be acknowledged or dismissed by right clicking on the alert and selecting the acknowledge of dismiss options. Once acknowledged, the alert will turn grey in the alert list to indicate the change in status. Dismissing an alert will acknowledge it and remove it from the alert list unless the underlying activity continues to update in which case the acknowledged alert will return. It is possible to select multiple alerts and acknowledge or dismiss them in one go. There is also an option to acknowledge or dismiss all alerts that currently exist.
It is recommended that the operator adds a comment to an alert to indicate why it was acknowledged or dismissed particularly for more serious alerts where the ability to understand the actions taken may be of interest in the future.
As well as being able to perform these actions from the right-click menu, icons are available in the toolkits on the main map display and alert list windows to provide the same functionality.
Tracked Alerts & Focus Events
The map, waterfall and alert displays can be configured to automatically track a specific alert or to react to a user highlighting/focusing on an alert or position.
Focus on Alert Use this option to reposition the map cursor when ‘Focus on Alert’ or ‘Focus on Position’ options are used.
Observe Tracked Alerts (Manual) If there is an active detection of high importance, users can select “track” via Alert Right Click Menu. Any displays with manually tracked alerts enabled will follow/track this alert. Once the Alert is completed (i.e. the event has ended) or dismissed it will no longer be tracked.
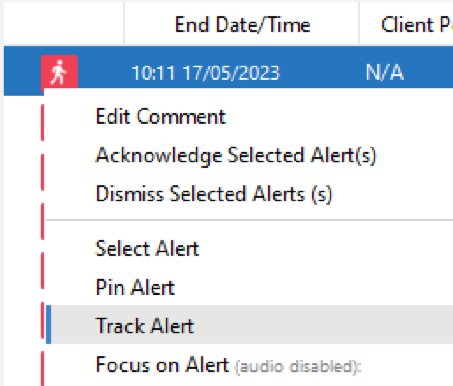
Observe Tracked Alerts (Auto)
If all high alerts are required to be tracked, the ‘Observe Track Alerts (Auto) can be selected. Any displays with ‘Observe Track Alerts (auto)’ enabled will track/follow any new high alert automatically.
These options are set on a per display basis (i.e. two waterfalls open with different option for each). The configured options will be remembered in a user’s profile.
Further details on the individual displays and how they react are detailed below.
Map and Waterfalls The map and waterfall displays will make use of the tracking options to reposition the focus of the map and waterfall based on the selected option.
Alert Displays
Alert displays will make use of the observe track options to pin tracked alerts at the top of the alert list so that they are always visible.
Historic Data Extraction
All historic alerts, audits and processing reports can be accessed on the Historical Analysis menu. The availability of historic data will vary with the system configuration.
The Historical Analysis menu provides access to various data:
- Historic Waterfall Data – Provides access to waterfall data for a specified time period as long as the data is available on the rolling recorders.
- Multi-Channel Trending - Allows plotting of time series data from the various rolling recorders.
- Historical Alerts - Provides the ability to search the database for alerts that have occurred within a specified time period.
- Audits - Allows auditing of all changes made to the system and by which user account.
- Process Metrics - Provides monitoring of the historic performance of the system processes.
Historical Waterfall Data
| Data Source | Allows the user to select the data source for the waterfall. | |
| Mouse Mode | Channel Zoom – Allows the user to zoom the waterfall. Audio - Allows the user to draw a path and replay the audio for the selected time period. Historical Analysis Channel – Opens an analysis window for the selected period and location. Measure Speed - allows the speed of an event to be measured in either, kph, m/s or mph | |
| Extract | FBE Data - extracts the FBE data for the selected period. Sensor Data - extracts the Sensor data for the selected period, within the limits specified in the System Architecture Specification. Waterfall Image - Extracts the image of the waterfall currently displayed | |
| Data Scale/View | Colour Scaling - Allows the user to change the colour scheme of the Historic waterfall Reset Zoom - Resets the zoom Level to default Zoom Out - Zoom out one level from the previous zoom Adjust Scale - Adjust the channel range and/or the start and end times Scale Colour On Data Load - Sets the colour scale automatically on opening |
The Historical Waterfall can be accessed from various areas of the system. Either directly via the Historical Analysis menu or from the right-click menu of a selected alert.
When accessed directly, select the required OPS, Rolling Recorder data type, date/time, and range of the data you wish to retrieve and then click search.
The Historic Waterfall Data will display the selected time and channel range as a waterfall in a new window.
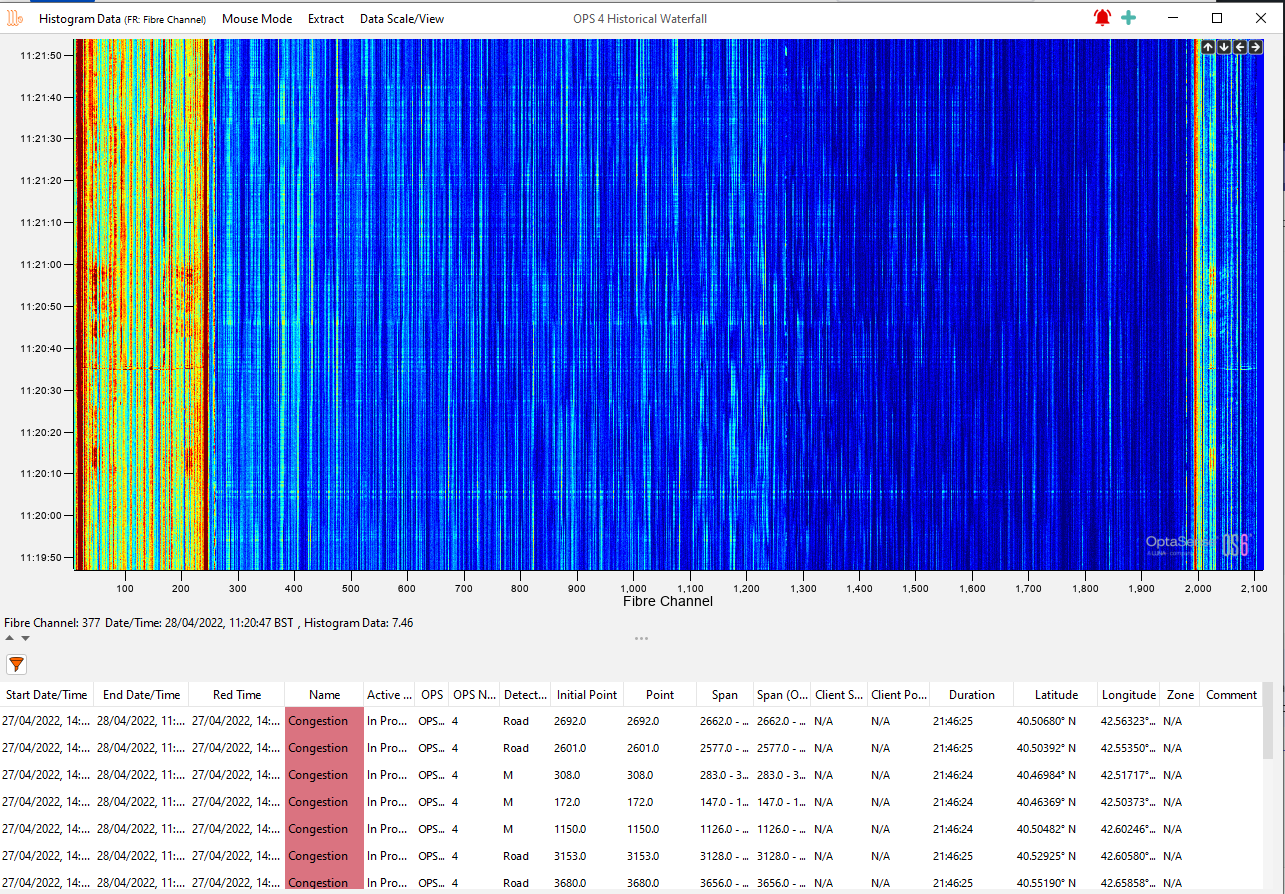
Alerts available within the selected span will be displayed at the bottom of the waterfall. By clicking on an alert from the list an icon indicating the alert location will appear on the waterfall along with any track information associated with the alert. Multiple alerts can be selected at once.
Multi-Channel Trending
The Multi-Channel Trending tool allows the user to plot time series for data stored on the rolling recorders for a specified time period. Data can be added to the display by selecting the “Add Source” and “Fibre Channel” options. The tool can also be accessed directly from the right-click menu on an alert where it will pre-populate with time series data for the alert channel and any relevant data sources. An example showing a time series of FBE data is shown below.
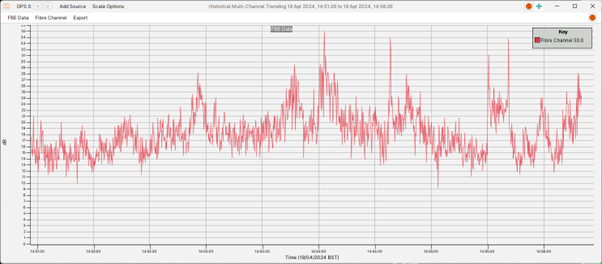
When accessed directly from an alert, the multi-channel trending tool will pre-populate with data associated with the alert. Additional data and locations can be manually added.
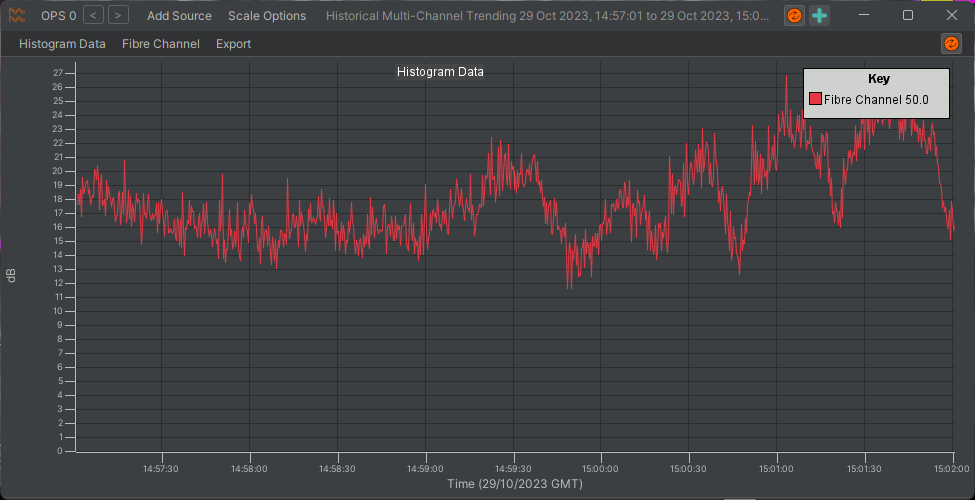
Historic Alerts and Reporting
This tool provides the ability to recall alerts that have been generated on the system. Displayed alerts can then be exported to CSV or into a HTML report containing several chart options.
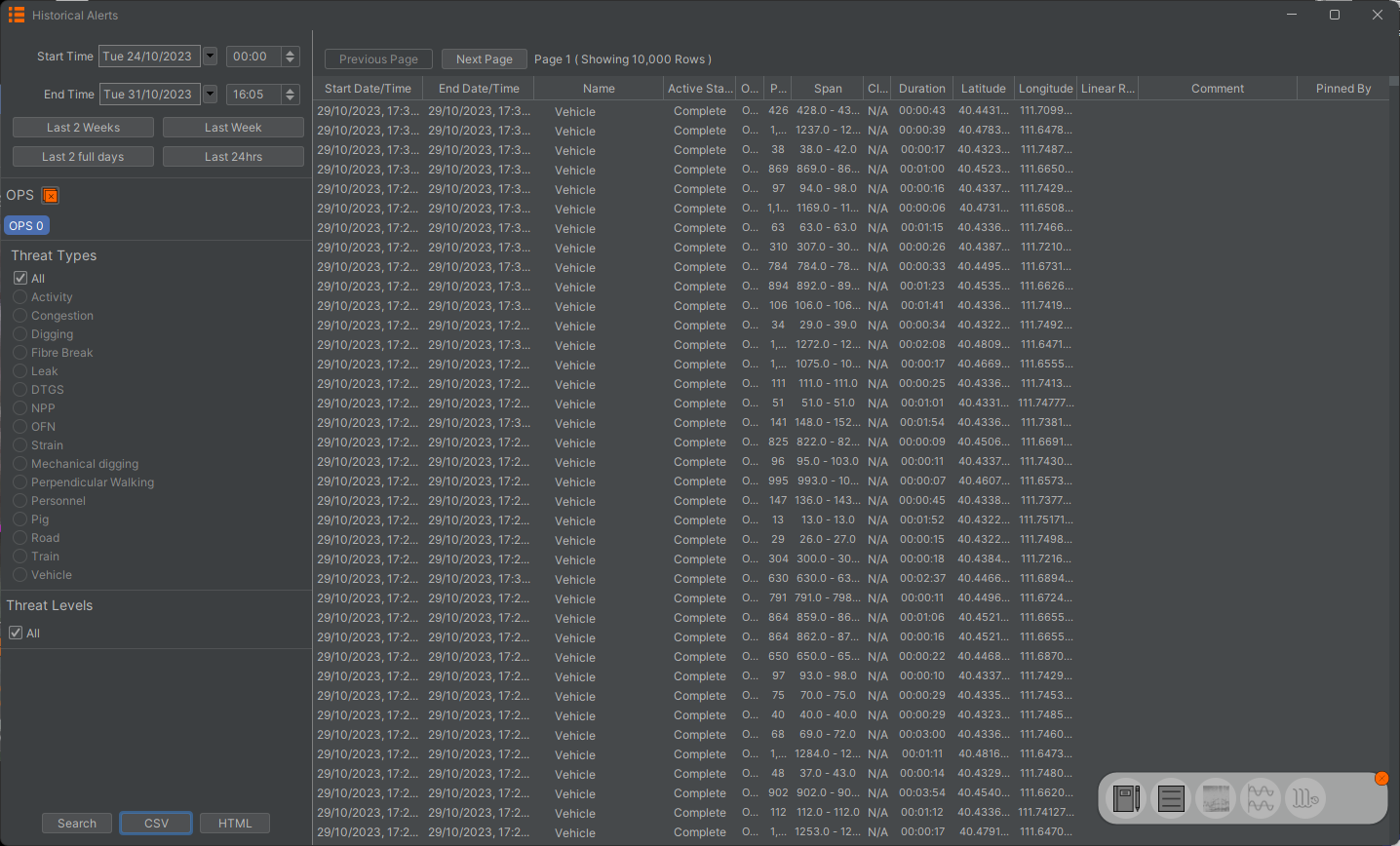
From the toolbar on the left side the user can select the duration the report should cover. The user can also select the level of alerts (low, medium or high), filter specific alert types, and span the search over multiple OPS. Press Search to run the report.
Once a report has been generated, the user can extract the report to either CSV or HTML format.
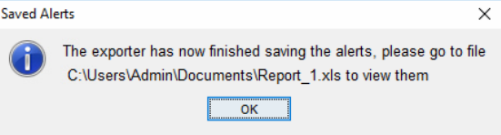
Report Extraction The CSV button will export alert data into Comma Separated Variable file format. Once the button is clicked, a prompt will ask you to confirm the export, select yes. Choose the desired location and click save. Another prompt will appear confirming that the export has finished.
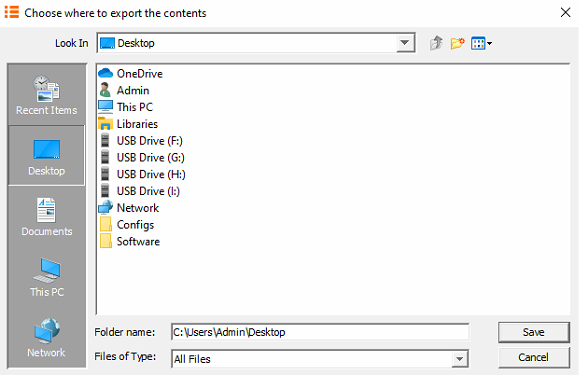
The HTML button will export the data into a web page format. Once the button is clicked, choose the desired location and select Open. Now select the required charts from the chart option dropdown box or select Add All. Select Generate to compile the report.

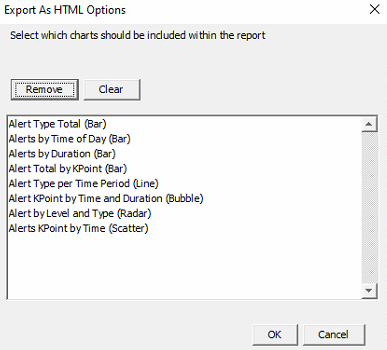
Once the report extraction is complete, it will produce a zipped file that will need to be unzipped in order to view the report.
Once extracted, navigate to the AlertReport.html file. Right click on it and open with a web browser.
HTML Report When viewing a HTML alert report, there will be several tabs on the top left of the browser.
-
OptaSense - Provides details about the software version and report contents
-
Charts -Displays a list of charts
-
Waterfall -Provides a histogram waterfall based on the duration selected in the alert search query.
-
View - View Mode: Selecting Default will change the view mode to extended. This provides increased viewing focus on charts.
Theme: Changes the white borders of the webpage to grey.
Chart Types
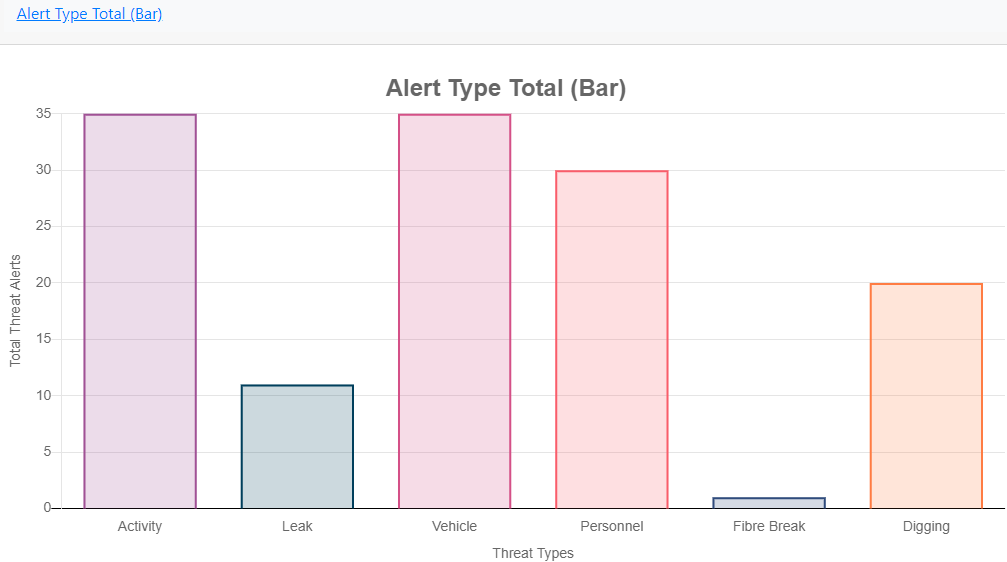
Alert Type Total (Bar)
Provides a bar chart of all alert types irrespective of level (High, medium & low).
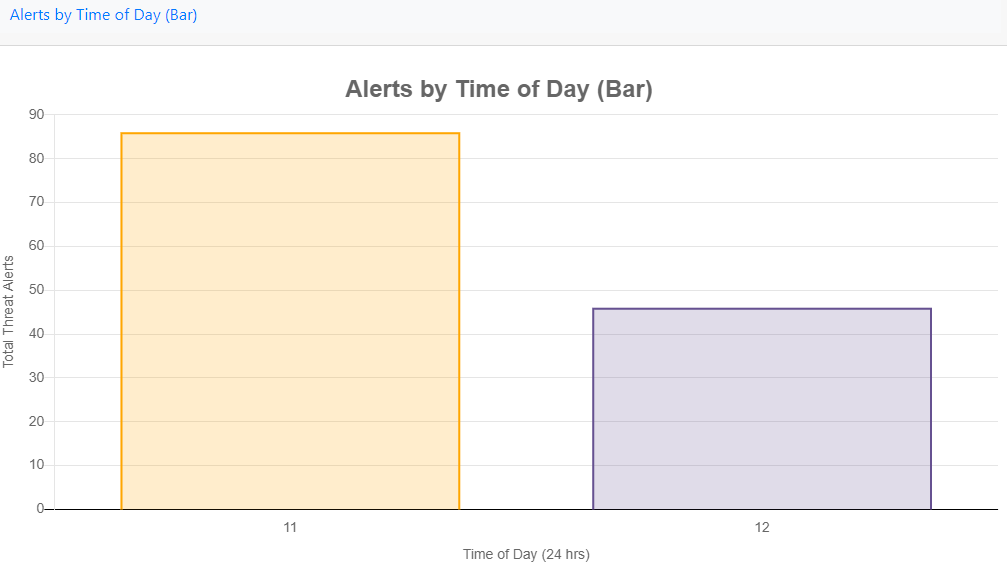
Alerts by Time of Day (Bar)
Displays a total number of alerts per time period (in this case hourly over 24 hours).
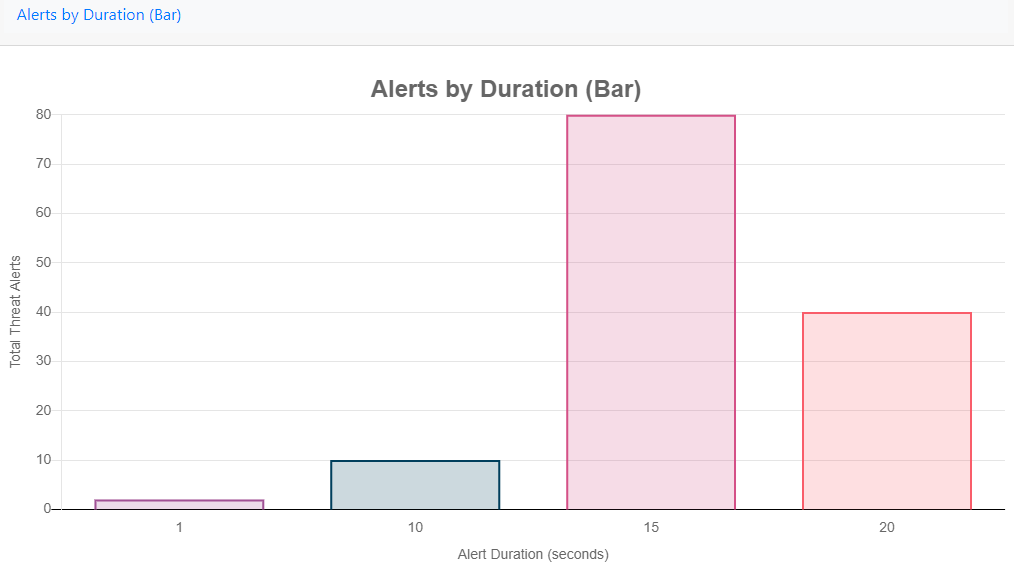
Alerts by Duration (Bar)
Gives an insight into how long the different alert types are updating for.
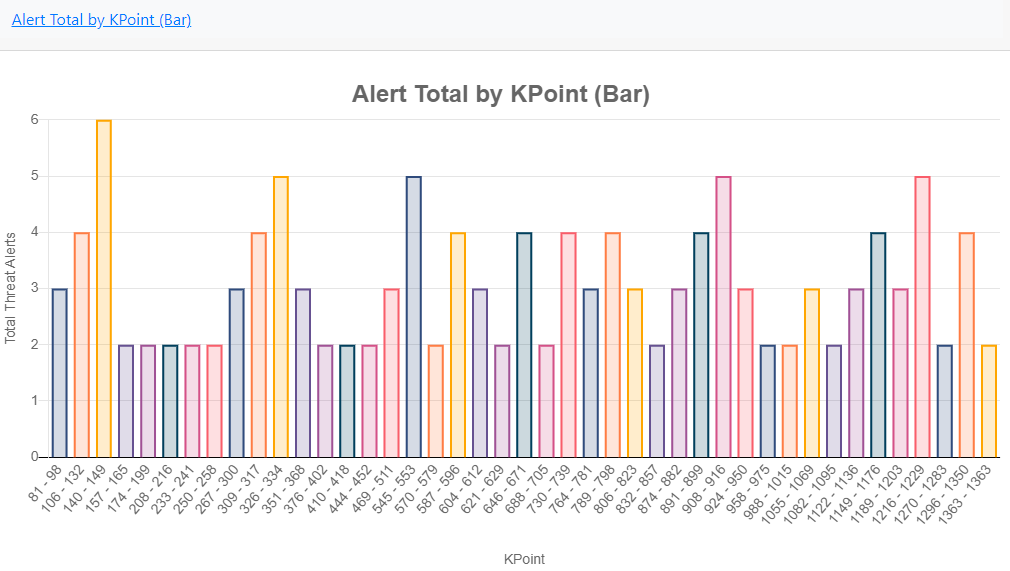
Alert Total by KPoint (Bar)
In this chart alerts are grouped and displayed against what K Points they were generated in.
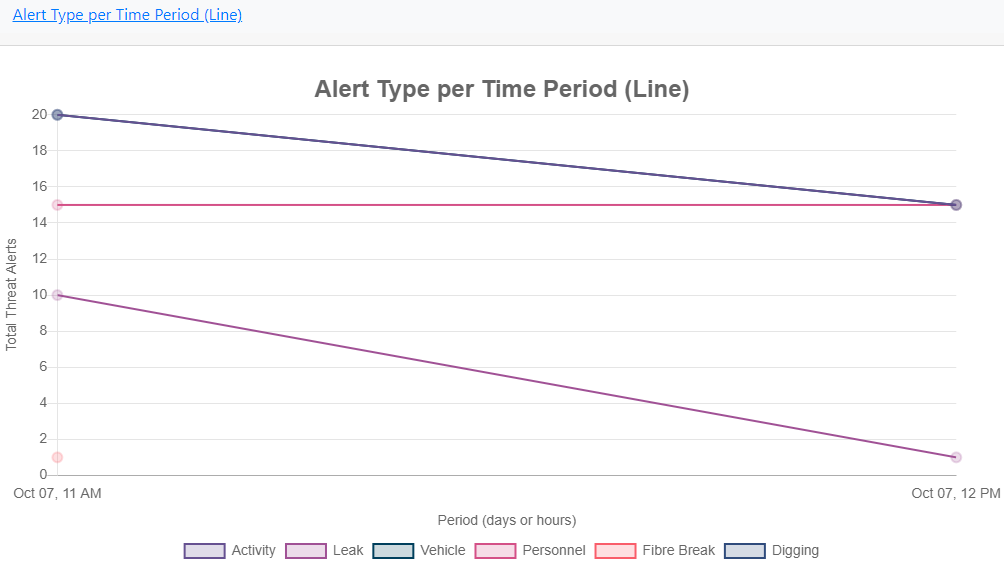
Alert Type per Time Period (Line)
Shows what alert types were raised over a time period (in this case over one hour) and whether that amount increased, decreased or stayed the same.
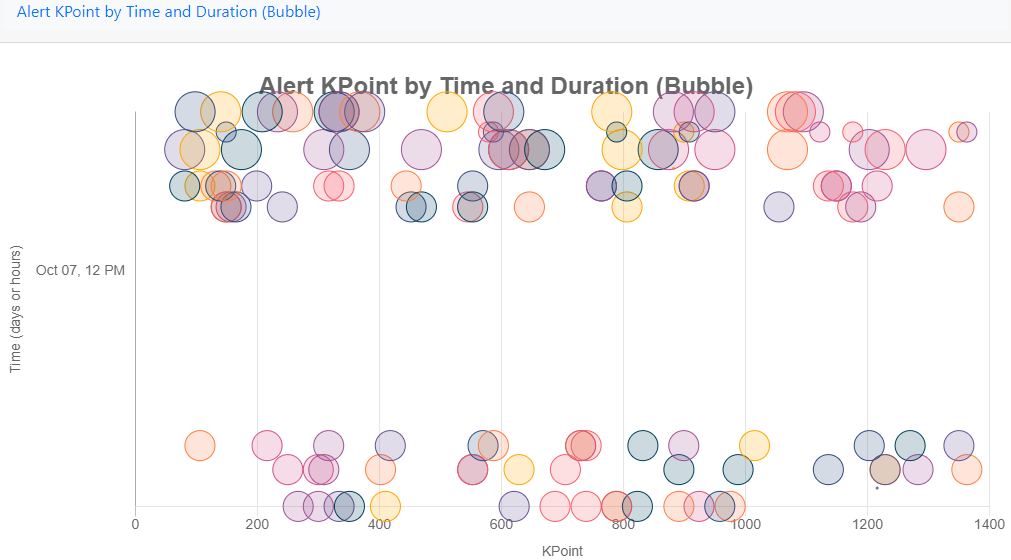
Alert KPoint by Time and Duration (Bubble)
Displays alerts against the KPoints that they were generated in and over what time period they occurred (in this example, over an hour). The bigger the bubble the longer the alerted lasted for.
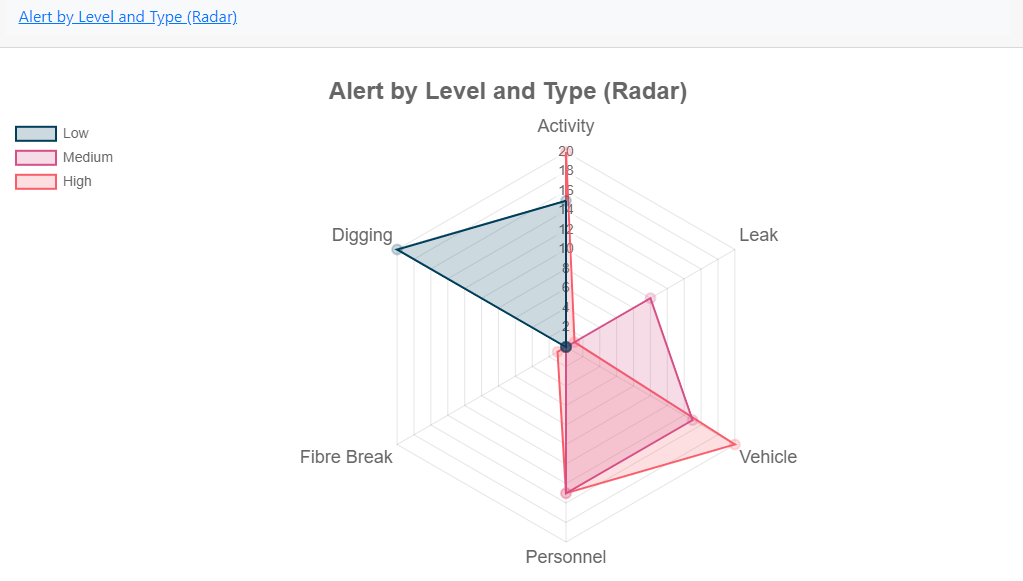
Alert by Level and Type (Radar)
Shows all alert types raised by type and level.
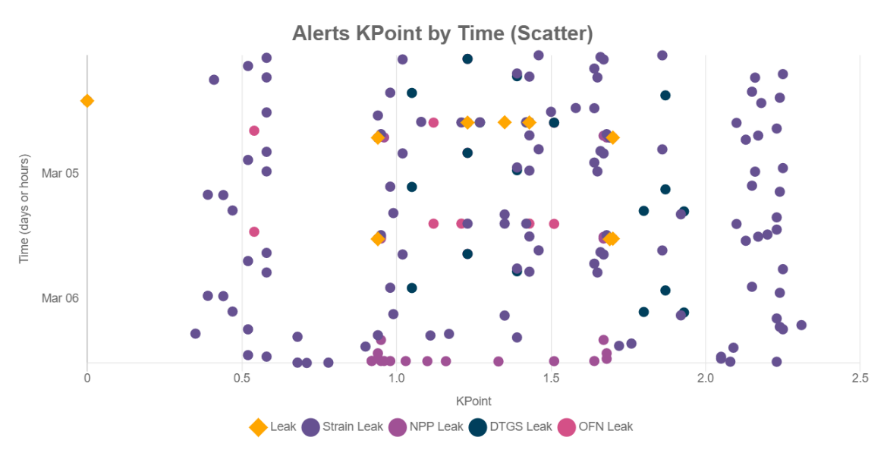
Alerts KPoint by Time (Scatter)
Displays alerts against what KPoint they were generated in and over what time period they occurred (in this example, over a day).
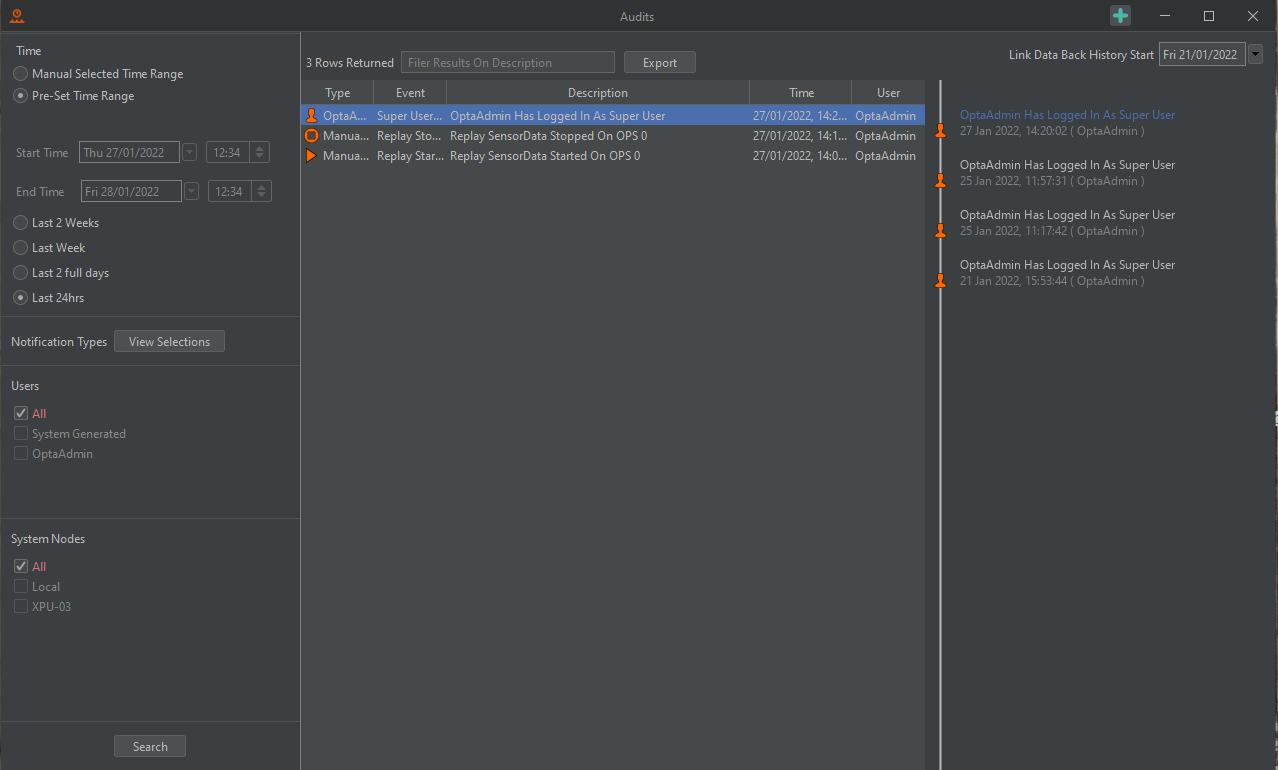
Audits
The audit function allows the user to audit all changes that were made to the system and who made them.
From the toolbar on the left of the audit tool, the user can specify the period of interest and configure what details are to be included in the audit.
To change what actions are to be listed, select View Selection as shown in the image above. Highlight the events to be audited as required.
Press Search to run the audit.
More information on each event can be accessed by hovering the mouse cursor over the event or by selecting it. Use the search box at the top of the audit tool to filter the events returned by the audit tool.
Process Metrics
Process report charting enable the user to select what resources they want to monitor. Explanations for each resource include,
- Memory %: This shows the systems demand on memory. The higher the red line the more the system is using.
- CPU %: This is the demand on system processing. The higher the red line, the harder the CPU is working to service the system.
- GC Throughput %: This depicts how well the system is cycling memory garbage collection. The lower the red line, the more the system is struggling to recycle the memory garbage.
- GC Pause Time Sec: This shows any pauses in the system dumping memory. The more consistent the red line the better the system is dumping its unwanted memory garbage.
Event Waterfall Examples
The following set of waterfall images illustrates the typical appearance of some alerts within the waterfall and histogram.
Manual Digging
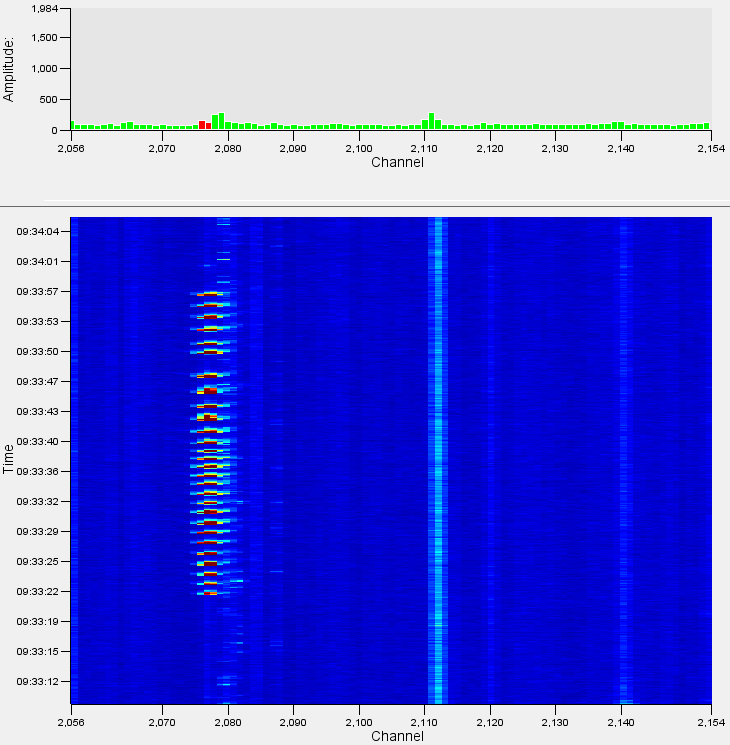
Manual digging comprises a series of short, sharp blows to the ground. These transient signals display as narrow bands of energy in the Y axis (time) but possibly broad in the X axis (distance / channel spread). Digging methods vary, however the signal will likely repeat – usually every few seconds – with regular breaks, changes in frequency, and duration, but generally over a prolonged period we are looking for a series of individual impacts centred on a specific channel. A farmer may make impacts but will move around – the malignant digger will be centred on a specific location. With digging times to get down a metre somewhere between 20 minutes and a couple of hours the concerted effort of manual digging is very clearly distinguished from benign background activity. The detector can also incorporate positive or negative filters against cattle movement or very periodic activity (e.g., pumps, water dripping, etc.) which are known to create nuisance alert states.
Personnel
Like manual digging, walking appears acoustically as a series of transient impacts on the ground. The acoustic energy levels are generally much lower, typically only covering one or two channels and not as large an amplitude, however, they are usually more regular and can contain a velocity component – particularly if someone is walking along or beside the fibre.
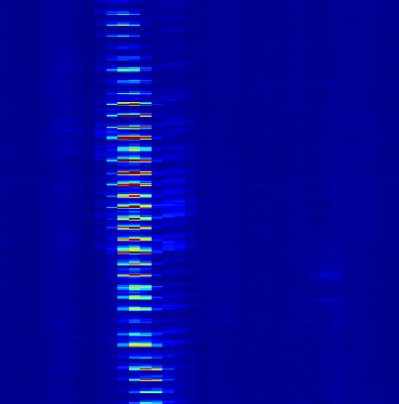
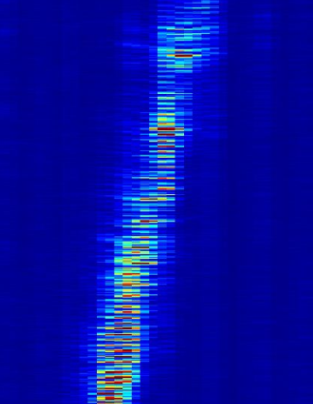
The clearest way to differentiate walking from any other digging activity is to listen to a channel with walking taking place – it is very clear from the low frequency thumps that the sound generated is being caused by footsteps and not any other activity. Footsteps crossing the fibre will be static within a channel or two but will increase in intensity and then fade away in a very characteristic manner. Running footsteps will appear more intense and will be faster.
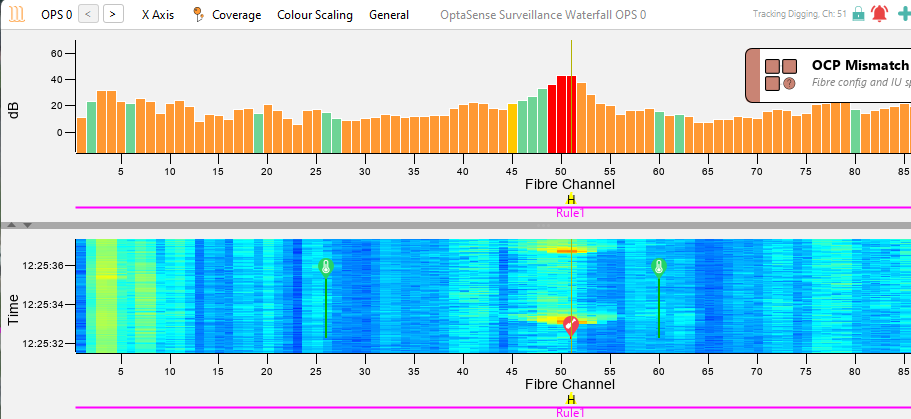
Vehicle
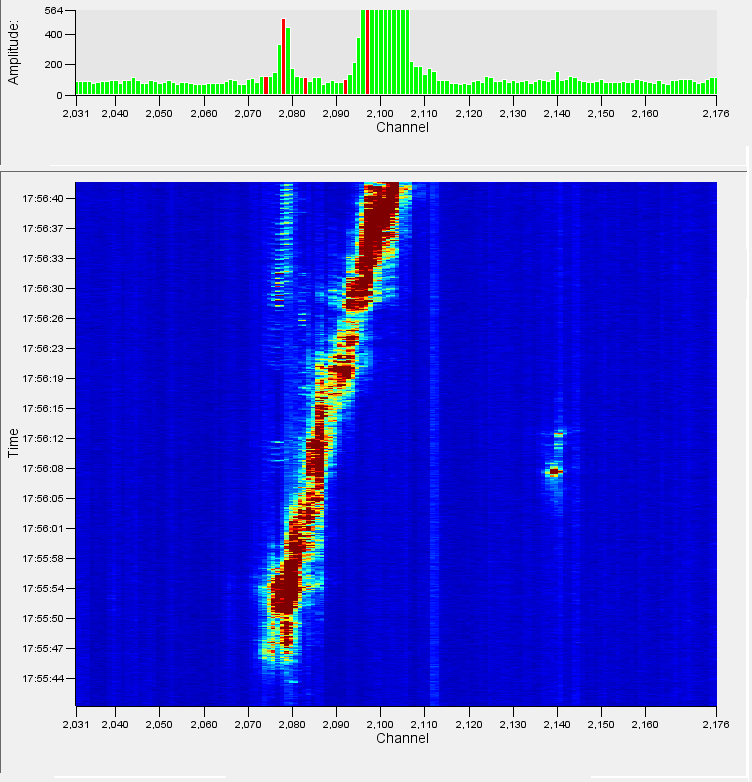
The figure above shows a vehicle travelling from left to right across the waterfall. This sort of signature is typical of a moving vehicle as there is a nearly constant signal (an unbroken line of increased noise) and is travelling at a sensible speed, in this case approximately 22kph. The intensity of the signal will vary with the size of the vehicle and its position relative to the fibre. This means that a large vehicle travelling offset from the fibre by some distance may look similar to a small vehicle travelling directly above the fibre. Similarly, the surface on which the vehicle is travelling will have an impact on the size of the signal, a vehicle moving quickly on rough ground will also create more signal than a slower moving vehicle.
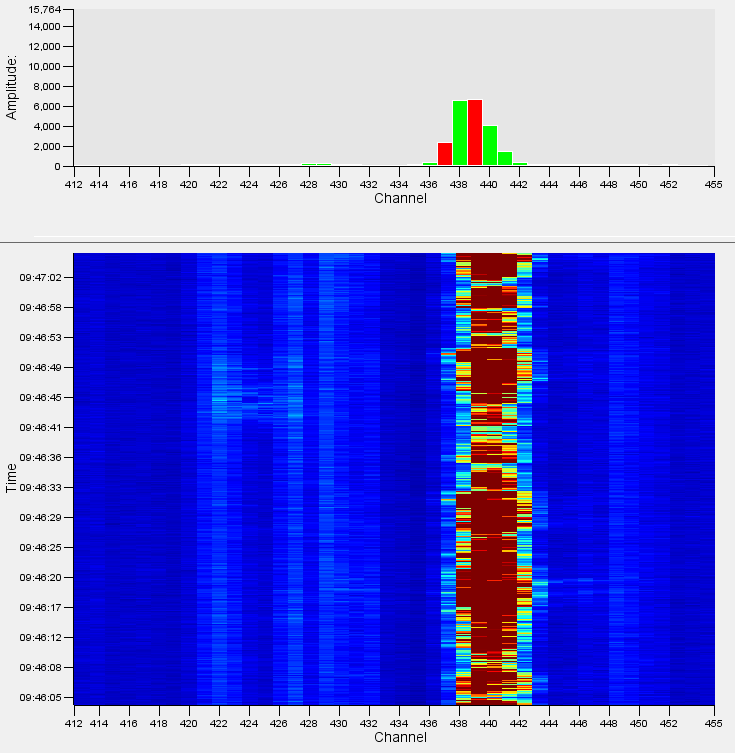
Mechanical Digging
The acoustic signature generated by a mechanical digging event comprises a transient digging signal (similar to a manual digging event) and a localised engine tonal. The mechanical digging detection algorithm looks for these two components in tandem in order to determine which events are mechanical digging and which are other forms of ground works. There are significant differences between the acoustic signatures of specific types of excavators and this is taken into consideration when tuning the detection algorithms, i.e., what excavators are typically used locally? Large, tracked excavators and small gas driven pneumatic excavators are very different acoustically, so part of the installation process is to identify these excavators and tune accordingly.
Activity Detector
The Activity detector is a versatile and powerful detection algorithm that can be tuned to alert on a variety of events. It is often used for detection of behaviours specific to an area, trenching machines or bulldozers for example. There are several different activity detectors, however the three most used are listed below.
General Activity - The General Activity detector is used as a “General Purpose” detector of abnormal activity. It looks for loud, prolonged acoustic events in the attempt to detect abnormal activity. For example, this detector could be triggered by bulldozers, trenching machines, Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) machines and piling.
Pipeline Activity - This algorithm is usually configured to detect any large-scale intrusions or events on a pipeline. Hot tap attempts often use tools such as drills and angle grinders to cut into the pipeline. These are localised, high energy acoustic signals that tend to last for short durations and are very different to surface based activities (digging, walking, etc).
Fence Activity - The Fence Activity algorithm is used for detection of threatening behaviour on perimeter or border fences. Typically, these activities include climbing, cutting, ladders and shaking (Figure 118). The Fence Activity detector is versatile enough to detect these activities but will require tuning for each activity defined by the client requirements or threat profile. Additional filtering is often applied to fence mounted systems to reduce the possibility of nuisance detections caused by weather.